“US Health Crisis Updates: Navigating Challenges and Seeking Solutions
Related Articles US Health Crisis Updates: Navigating Challenges and Seeking Solutions
- The Midwest Tornado Outbreak: A Chronicle Of Destruction And Resilience
- Host-Based Security: The Ultimate Guide to Securing Your Servers
- Effective Cyber Defense Strategies for Enhanced Cybersecurity
- College Campus Protests: A Crucible Of Change, Controversy, And Civic Engagement
- The United States’ Funding Contribution To The World Health Organization: A Complex And Evolving Relationship
Introduction
On this special occasion, we are happy to review interesting topics related to US Health Crisis Updates: Navigating Challenges and Seeking Solutions. Let’s knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
US Health Crisis Updates: Navigating Challenges and Seeking Solutions
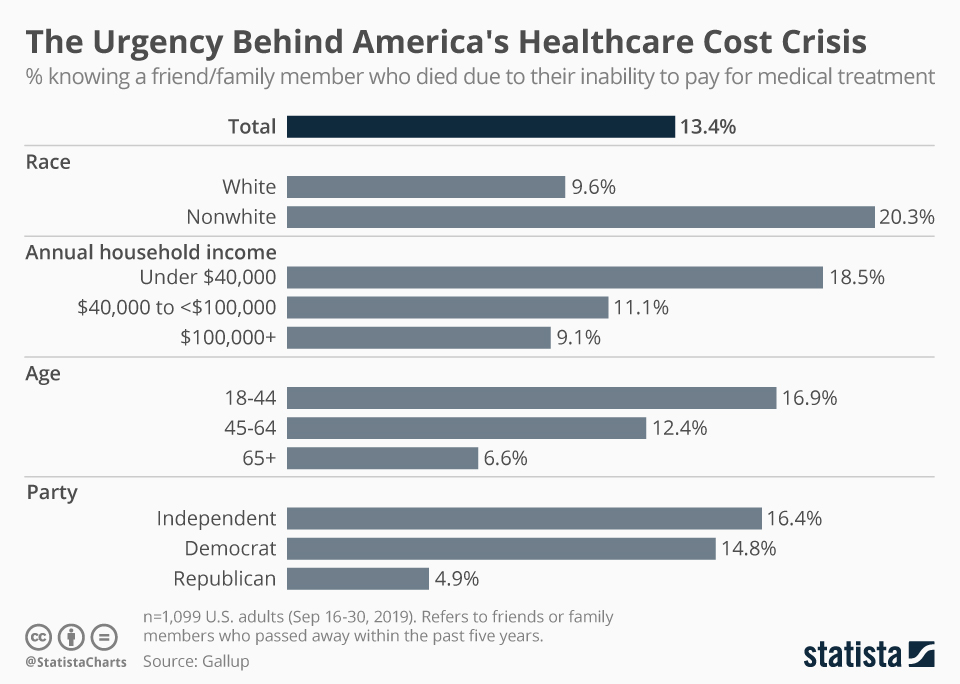
The United States healthcare system, renowned for its technological advancements and specialized care, is simultaneously grappling with a multitude of complex challenges that have coalesced into a multifaceted health crisis. This crisis encompasses issues such as rising costs, unequal access to care, chronic diseases, mental health concerns, and public health emergencies. Understanding the nuances of these challenges is crucial for policymakers, healthcare professionals, and the public to collaborate on effective solutions.
Rising Healthcare Costs:
One of the most pressing issues in the US healthcare system is the ever-increasing cost of medical services, prescription drugs, and insurance premiums. The United States spends a significantly larger portion of its GDP on healthcare compared to other developed nations, yet health outcomes often lag behind. Several factors contribute to this problem:
-
Fee-for-Service Model: The dominant fee-for-service payment model incentivizes healthcare providers to deliver more services, regardless of their necessity or effectiveness. This can lead to overutilization and unnecessary procedures, driving up costs.
-
Administrative Complexity: The US healthcare system involves a complex web of insurance companies, billing processes, and regulatory requirements. This administrative burden increases overhead costs for providers and insurers, which are then passed on to consumers.
-
Pharmaceutical Prices: Prescription drug prices in the United States are significantly higher than in other countries. Pharmaceutical companies have considerable power to set prices, and limited government regulation allows them to maximize profits.
-
Lack of Price Transparency: Patients often lack clear information about the costs of medical services before receiving them. This lack of transparency makes it difficult for consumers to make informed decisions and negotiate prices.
-
Chronic Diseases: The prevalence of chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and obesity is rising in the United States. Managing these conditions requires ongoing medical care, medication, and lifestyle changes, which can be costly for both individuals and the healthcare system.
Unequal Access to Care:
Disparities in access to healthcare are a significant concern in the United States. Millions of Americans lack health insurance, and even those with insurance may face barriers to accessing timely and affordable care. Factors contributing to unequal access include:
-
Insurance Coverage: The Affordable Care Act (ACA) has expanded health insurance coverage to millions of Americans, but gaps remain. Some individuals are still uninsured due to factors such as affordability, immigration status, or lack of awareness about available options.
-
Geographic Location: Rural areas often have a shortage of healthcare providers and facilities. This can make it difficult for residents to access primary care, specialty services, and emergency care.
-
Socioeconomic Status: Low-income individuals and families may struggle to afford healthcare services, even with insurance. They may also face barriers such as transportation difficulties, language barriers, and lack of childcare.
-
Racial and Ethnic Disparities: Racial and ethnic minorities often experience poorer health outcomes and face barriers to accessing quality healthcare. These disparities are rooted in historical and ongoing discrimination, socioeconomic factors, and cultural differences.
-
Language Barriers: Individuals with limited English proficiency may struggle to navigate the healthcare system and communicate effectively with providers. This can lead to misunderstandings, errors in diagnosis and treatment, and reduced access to care.
Chronic Diseases:
Chronic diseases are a leading cause of death and disability in the United States. The most common chronic diseases include heart disease, stroke, cancer, diabetes, and chronic respiratory diseases. Several factors contribute to the rise in chronic diseases:
-
Lifestyle Factors: Unhealthy lifestyle choices such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, tobacco use, and excessive alcohol consumption increase the risk of developing chronic diseases.
-
Aging Population: As the US population ages, the prevalence of chronic diseases is expected to increase. Older adults are more likely to develop chronic conditions due to age-related changes in the body.
-
Environmental Factors: Exposure to environmental toxins such as air pollution, water contamination, and hazardous substances can increase the risk of certain chronic diseases.
-
Socioeconomic Factors: Poverty, lack of education, and limited access to healthy food and safe environments can contribute to the development of chronic diseases.
-
Genetics: Genetic factors can play a role in the development of some chronic diseases. Individuals with a family history of certain conditions may be at higher risk.
Mental Health Concerns:
Mental health is an integral part of overall health and well-being. However, mental health concerns are often stigmatized and under-addressed in the United States. Millions of Americans experience mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia. Factors contributing to mental health concerns include:
-
Stigma: Stigma surrounding mental illness can prevent individuals from seeking help. Many people fear judgment or discrimination if they disclose their mental health struggles.
-
Access to Care: Access to mental health services is limited in many areas of the United States. There is a shortage of mental health professionals, and many people lack insurance coverage for mental health treatment.
-
Socioeconomic Factors: Poverty, unemployment, and social isolation can increase the risk of mental health problems.
-
Trauma: Traumatic experiences such as abuse, violence, and natural disasters can have a lasting impact on mental health.
-
Substance Abuse: Substance abuse and mental health disorders often co-occur. Individuals with substance abuse problems are at higher risk of developing mental health conditions, and vice versa.
Public Health Emergencies:
The United States has faced several public health emergencies in recent years, including the COVID-19 pandemic, opioid crisis, and outbreaks of infectious diseases. These emergencies have strained the healthcare system and highlighted the need for improved public health preparedness and response.
-
COVID-19 Pandemic: The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on the United States, causing widespread illness, death, and economic disruption. The pandemic has exposed weaknesses in the public health system, including inadequate testing capacity, supply chain shortages, and disparities in access to care.
-
Opioid Crisis: The opioid crisis continues to be a major public health concern in the United States. Overdose deaths involving opioids have skyrocketed in recent years, driven by the misuse of prescription pain medications and the rise of illicit fentanyl.
-
Infectious Disease Outbreaks: The United States has experienced outbreaks of infectious diseases such as measles, mumps, and Zika virus in recent years. These outbreaks highlight the importance of vaccination and public health surveillance.
Seeking Solutions:
Addressing the US health crisis requires a multifaceted approach involving policy changes, healthcare system reforms, and individual actions. Some potential solutions include:
-
Value-Based Care: Transitioning from a fee-for-service model to a value-based care model can incentivize healthcare providers to deliver high-quality, cost-effective care. Value-based care models reward providers for achieving positive health outcomes rather than simply providing more services.
-
Price Transparency: Increasing price transparency in healthcare can empower consumers to make informed decisions and negotiate prices. Requiring hospitals and other providers to disclose their prices can help to lower costs.
-
Prescription Drug Reform: Implementing policies to lower prescription drug prices can make medications more affordable for patients. Options include allowing Medicare to negotiate drug prices, importing drugs from other countries, and promoting the development of generic drugs.
-
Expanding Access to Care: Expanding access to health insurance and healthcare services can improve health outcomes and reduce disparities. Options include strengthening the Affordable Care Act, expanding Medicaid, and investing in community health centers.
-
Preventive Care: Investing in preventive care can help to prevent chronic diseases and reduce healthcare costs. Promoting healthy lifestyle choices, providing vaccinations, and screening for diseases can improve health outcomes.
-
Mental Health Integration: Integrating mental health services into primary care settings can improve access to care and reduce stigma. Training primary care providers to screen for and treat mental health conditions can help to address the mental health crisis.
-
Public Health Preparedness: Strengthening public health preparedness and response can help to prevent and mitigate the impact of public health emergencies. Investing in public health infrastructure, training healthcare professionals, and developing emergency response plans can improve the nation’s ability to respond to future crises.
The US health crisis is a complex and multifaceted challenge that requires a comprehensive and collaborative approach. By addressing issues such as rising costs, unequal access to care, chronic diseases, mental health concerns, and public health emergencies, the United States can improve the health and well-being of its citizens.
