“State Governors Respond to Federal Cuts: A Patchwork of Strategies and Concerns
Related Articles State Governors Respond to Federal Cuts: A Patchwork of Strategies and Concerns
- The Supreme Court And Affirmative Action: A Shifting Landscape Of Equal Opportunity
- Chelsea Vs Liverpool: A Tactical Showdown Ends In A Thrilling Draw
- Crypto Market Structure Bill: A Transformative Step Or Regulatory Overreach?
- Mastering Security Incident Handling: A Comprehensive Guide to Protect Your Cybersecurity
- Emil Bove Orders Dismissal Of Corruption Charges: A Detailed Analysis
Introduction
We will be happy to explore interesting topics related to State Governors Respond to Federal Cuts: A Patchwork of Strategies and Concerns. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
State Governors Respond to Federal Cuts: A Patchwork of Strategies and Concerns
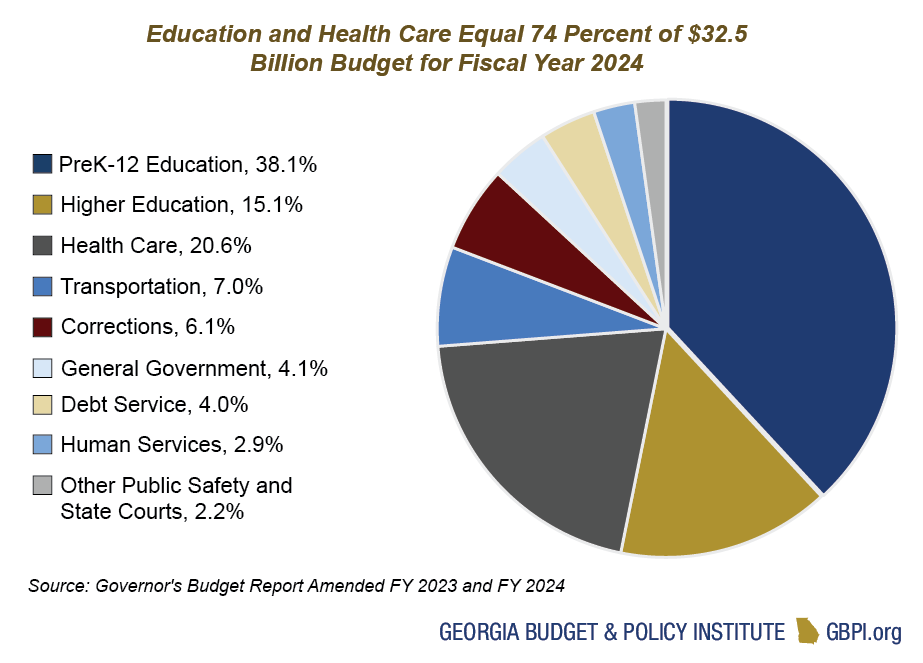
The relationship between the federal government and state governments in the United States is complex, characterized by both cooperation and conflict. Federal funding plays a critical role in supporting a wide range of state programs, from education and healthcare to infrastructure and public safety. When the federal government reduces its financial commitments to the states, the impact can be significant, forcing governors and state legislatures to make difficult choices about how to balance their budgets and meet the needs of their constituents.
The Landscape of Federal Funding to States
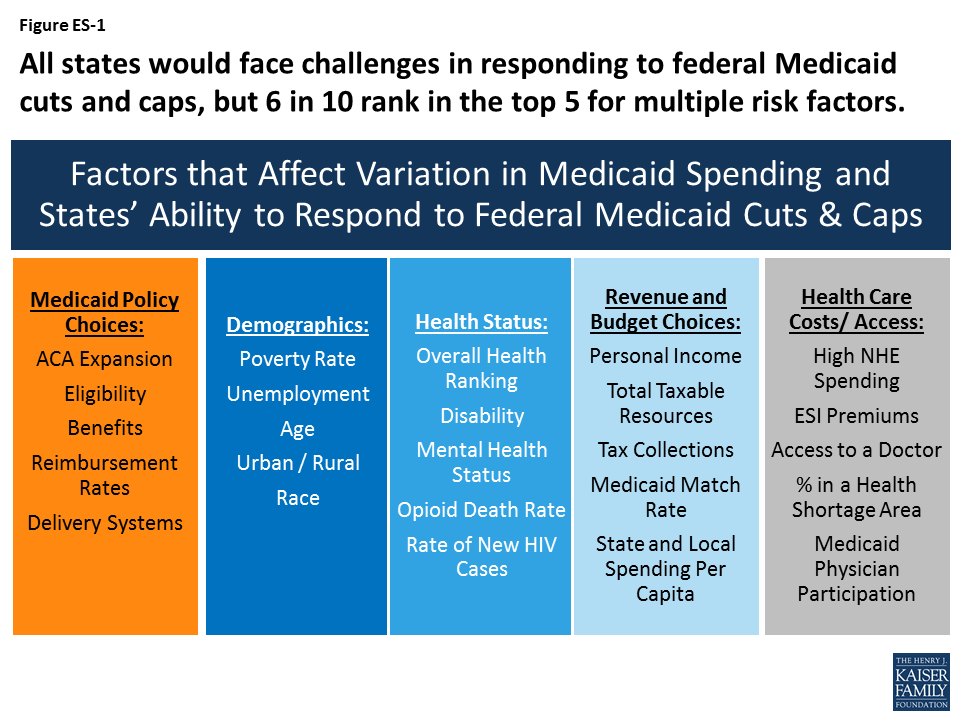
Federal funding to states comes in various forms, including grants, reimbursements, and direct payments. These funds are typically earmarked for specific purposes, such as Medicaid, highway construction, or environmental protection. The amount of federal funding that each state receives varies depending on factors such as population size, economic conditions, and the specific programs that the state participates in.
Over the years, federal funding to states has fluctuated depending on the priorities of the federal government and the overall economic climate. During times of economic recession, for example, the federal government may increase funding to states to help them cope with increased demand for social services. Conversely, during periods of fiscal austerity, the federal government may reduce funding to states in an effort to balance the federal budget.
The Impact of Federal Cuts on State Budgets
When the federal government cuts funding to states, the immediate impact is on state budgets. State governments must find ways to make up for the lost revenue, either by cutting spending, raising taxes, or a combination of both. The choices that governors and state legislatures make in response to federal cuts can have significant consequences for the services that states provide to their residents.
One of the most common responses to federal cuts is to reduce spending on state programs. This can involve cutting funding for education, healthcare, social services, and other essential programs. In some cases, states may also be forced to lay off state employees or reduce their salaries.
Another option for states is to raise taxes. This can be a politically unpopular choice, but it may be necessary to maintain essential services. States can raise taxes in a variety of ways, such as increasing income taxes, sales taxes, or property taxes.
In some cases, states may also try to find creative solutions to make up for lost federal funding. For example, states may partner with private organizations to provide services or find ways to streamline government operations to reduce costs.
Governors’ Responses: A State-by-State Perspective
The way that governors respond to federal cuts varies depending on the political and economic context of their states. Governors from different parties may have different priorities and different ideas about how to best address budget shortfalls.
In states with strong economies and healthy budget surpluses, governors may be able to absorb federal cuts without making significant changes to state programs. However, in states with struggling economies and tight budgets, federal cuts can have a much more dramatic impact.
Here are a few examples of how governors have responded to federal cuts in recent years:
-
California: In response to federal cuts to healthcare funding, Governor Gavin Newsom has proposed expanding the state’s own healthcare programs to ensure that all Californians have access to affordable healthcare. He has also advocated for increased federal funding for Medicaid.
-
Texas: Governor Greg Abbott has criticized federal cuts to border security funding and has called on the federal government to increase its support for border security efforts. He has also signed legislation to increase state funding for border security.
-
New York: Governor Kathy Hochul has expressed concerns about the impact of federal cuts on the state’s ability to provide essential services to its residents. She has called on the federal government to work with states to find solutions to address budget shortfalls.
-
Florida: Governor Ron DeSantis has taken a more confrontational approach to federal cuts, challenging the federal government’s authority in areas such as environmental regulation and healthcare policy. He has also signed legislation to reduce state reliance on federal funding.
The Political Dimensions of Federal-State Relations
The relationship between state governors and the federal government is inherently political. Governors often find themselves caught between the need to advocate for their state’s interests and the desire to maintain a good working relationship with the federal government.
When the federal government is controlled by a different party than the state government, the potential for conflict is even greater. In these situations, governors may be more likely to criticize federal policies and challenge federal authority.
However, even when the federal government and the state government are controlled by the same party, there can still be disagreements over funding priorities and policy issues. Governors must balance the needs of their constituents with the priorities of their party.
The Long-Term Implications of Federal Cuts
The long-term implications of federal cuts on state governments are significant. When states are forced to cut spending on essential programs, it can have a negative impact on the health, education, and well-being of their residents. Federal cuts can also make it more difficult for states to invest in infrastructure and economic development, which can hinder long-term economic growth.
In addition, federal cuts can strain the relationship between the federal government and state governments, leading to increased conflict and distrust. This can make it more difficult for the two levels of government to work together to address common challenges.
Strategies for Navigating Federal Cuts
Given the potential impact of federal cuts, state governments must develop strategies for navigating these challenges. Some potential strategies include:
-
Diversifying Revenue Streams: States can reduce their reliance on federal funding by diversifying their revenue streams. This can involve increasing state taxes, implementing new fees, or finding new sources of revenue, such as tourism or natural resource extraction.
-
Improving Efficiency and Effectiveness: States can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of their programs to reduce costs and make the most of limited resources. This can involve streamlining government operations, implementing new technologies, or partnering with private organizations.
-
Advocating for Increased Federal Funding: States can advocate for increased federal funding for programs that are important to their residents. This can involve lobbying members of Congress, working with other states to build coalitions, or raising public awareness about the impact of federal cuts.
-
Building Stronger Relationships with the Federal Government: States can build stronger relationships with the federal government to improve communication and cooperation. This can involve working with federal agencies to find solutions to common problems or participating in federal task forces and advisory committees.
-
Investing in Prevention and Early Intervention: States can invest in prevention and early intervention programs to reduce the need for more expensive services in the future. For example, investing in early childhood education can reduce the need for special education services later on.
Conclusion
Federal cuts pose a significant challenge to state governments, forcing them to make difficult choices about how to balance their budgets and meet the needs of their constituents. The way that governors respond to federal cuts varies depending on the political and economic context of their states, but all governors must find ways to mitigate the impact of these cuts on their residents.
By diversifying revenue streams, improving efficiency, advocating for increased federal funding, building stronger relationships with the federal government, and investing in prevention and early intervention, state governments can navigate the challenges of federal cuts and ensure that they continue to provide essential services to their residents. The ongoing dialogue and negotiation between state and federal leaders will continue to shape the landscape of public policy and resource allocation in the United States.