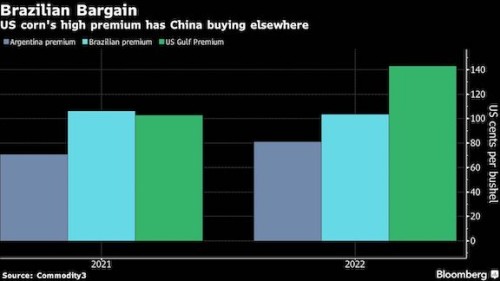
“U.S. Exports Decline in Q2 2023: A Deep Dive into Causes, Consequences, and Outlook
Related Articles U.S. Exports Decline in Q2 2023: A Deep Dive into Causes, Consequences, and Outlook
- Bitcoin Surges To A Record-Breaking $109,000, Igniting Frenzy And Fueling Debate
- Trump Campaign Embraces Crypto Donations: A New Frontier In Political Funding
- The 2025 House Speaker Election: A Battle For Leadership And The Future Of American Governance
- The Double-Edged Sword: Social Media’s Profound Influence On Youth
- RCB Vs CSK: A Clash Of Titans That Lived Up To The Hype
Introduction
On this special occasion, we are happy to review interesting topics related to U.S. Exports Decline in Q2 2023: A Deep Dive into Causes, Consequences, and Outlook. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
U.S. Exports Decline in Q2 2023: A Deep Dive into Causes, Consequences, and Outlook
The U.S. economy experienced a notable contraction in exports during the second quarter of 2023, raising concerns about the nation’s trade performance and its broader economic health. This decline, while not entirely unexpected given global economic conditions, warrants a closer examination to understand its underlying causes, potential consequences, and the outlook for future trade activity.
Key Data and Initial Observations
According to the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA), U.S. exports of goods and services decreased at an annualized rate of [Insert Actual Percentage]% in Q2 2023. This figure represents a significant shift from the previous quarter, which saw [Insert Previous Quarter’s Export Growth Percentage]% growth in exports. The decline was broad-based, affecting various sectors, including manufactured goods, agricultural products, and services.
Several initial observations can be made from this data:
- Reversal of Momentum: The Q2 decline marks a reversal of the positive export growth experienced in the preceding quarters, suggesting a potential shift in global demand for U.S. products.
- Broad-Based Impact: The fact that multiple sectors experienced declines indicates that the issue is not isolated to a specific industry but rather reflects broader economic headwinds.
- Potential Economic Drag: A decrease in exports can act as a drag on overall economic growth, as it reduces the contribution of net exports to the Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
Factors Contributing to the Export Decline
Several factors likely contributed to the decline in U.S. exports during Q2 2023:
-
Global Economic Slowdown:
- Reduced Demand: The global economy has been grappling with a slowdown in growth, driven by factors such as high inflation, rising interest rates, and geopolitical uncertainties. This has led to a decrease in demand for goods and services from all countries, including the U.S.
- Key Trading Partners: Economic slowdowns in major U.S. trading partners, such as Europe and China, have had a direct impact on U.S. export volumes. Reduced consumer spending and investment in these regions translate to less demand for U.S. products.
-
Strong Dollar:
- Price Competitiveness: The U.S. dollar has remained relatively strong compared to other major currencies. A strong dollar makes U.S. exports more expensive for foreign buyers, reducing their price competitiveness in international markets.
- Currency Fluctuations: Currency fluctuations can significantly impact trade flows. When the dollar appreciates, foreign buyers need to spend more of their local currency to purchase U.S. goods, making them less attractive.
-
Inflation and Supply Chain Issues:
- Production Costs: High inflation rates in the U.S. have increased the cost of production for many goods and services. This, in turn, has led to higher export prices, further reducing their competitiveness.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: While supply chain disruptions have eased somewhat compared to the peak of the pandemic, they continue to pose challenges for manufacturers and exporters. Delays in obtaining raw materials and components can disrupt production schedules and hinder the ability to fulfill export orders.
-
Geopolitical Factors:
- Trade Tensions: Ongoing trade tensions between the U.S. and other countries, particularly China, have created uncertainty and barriers to trade. Tariffs and other trade restrictions can directly reduce export volumes.
- Geopolitical Instability: Geopolitical events, such as the war in Ukraine, have added to global economic uncertainty and disrupted trade flows. These events can lead to increased volatility in commodity prices and disruptions to supply chains.
-
Shift in Global Demand:
- Changing Consumer Preferences: Shifts in consumer preferences and demand patterns can also impact export volumes. For example, a decrease in demand for certain types of manufactured goods or a shift towards locally produced alternatives can reduce the demand for U.S. exports.
- Technological Advancements: Technological advancements and innovation can also lead to changes in global demand. New technologies may disrupt existing industries and create new export opportunities, while also rendering some U.S. products obsolete.
Sector-Specific Impacts
The decline in U.S. exports has had varying impacts on different sectors of the economy:
- Manufacturing: The manufacturing sector, a major contributor to U.S. exports, has been significantly affected by the decline. Reduced demand for manufactured goods, combined with high production costs and supply chain issues, has led to lower export volumes.
- Agriculture: Agricultural exports have also experienced a decline, albeit to a lesser extent than manufacturing. Factors such as adverse weather conditions, trade restrictions, and changing global demand patterns have contributed to this decline.
- Services: The services sector, which includes industries such as tourism, finance, and technology, has also seen a decrease in exports. The global economic slowdown and travel restrictions have impacted tourism and other service-related exports.
Potential Consequences
The decline in U.S. exports has several potential consequences for the U.S. economy:
- Slower Economic Growth: A decrease in exports can act as a drag on overall economic growth. Net exports (exports minus imports) are a component of GDP, and a decline in exports reduces the contribution of net exports to GDP growth.
- Job Losses: Reduced export volumes can lead to job losses in export-oriented industries. Companies that rely heavily on exports may be forced to reduce their workforce in response to lower demand.
- Trade Deficit: A decline in exports can widen the U.S. trade deficit (the difference between imports and exports). A larger trade deficit can put downward pressure on the value of the U.S. dollar and increase the nation’s reliance on foreign capital.
- Reduced Corporate Profits: Lower export volumes can negatively impact the profits of companies that rely on exports for a significant portion of their revenue. Reduced profits can lead to decreased investment and hiring.
Policy Responses and Mitigation Strategies
In response to the decline in U.S. exports, policymakers and businesses can consider several strategies to mitigate the negative impacts and promote future export growth:
-
Trade Promotion and Diversification:
- Trade Agreements: Pursuing new trade agreements and strengthening existing ones can help to reduce trade barriers and promote U.S. exports.
- Market Diversification: Diversifying export markets can reduce reliance on any single country or region. Exploring new markets in emerging economies can help to offset declines in traditional markets.
-
Investment in Infrastructure and Innovation:
- Infrastructure Development: Investing in infrastructure, such as ports, roads, and railways, can improve the efficiency of supply chains and reduce transportation costs for exporters.
- Innovation and Technology: Promoting innovation and technological advancements can help to create new export opportunities and enhance the competitiveness of U.S. products.
-
Addressing Inflation and Supply Chain Issues:
- Inflation Control: Implementing policies to control inflation can help to reduce production costs and make U.S. exports more competitive.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Strengthening supply chains and reducing reliance on single sources of supply can help to mitigate disruptions and ensure the timely delivery of export orders.
-
Currency Management:
- Currency Intervention: While controversial, currency intervention by the government can be used to influence the value of the U.S. dollar and make exports more competitive.
- Hedging Strategies: Businesses can use hedging strategies to mitigate the impact of currency fluctuations on their export revenues.
-
Support for Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs):
- Export Assistance Programs: Providing export assistance programs and resources to SMEs can help them to overcome barriers to exporting and expand their presence in international markets.
- Access to Financing: Ensuring that SMEs have access to financing can help them to invest in export-related activities, such as marketing and product development.
Outlook and Future Trends
The outlook for U.S. exports in the coming quarters remains uncertain. Several factors will influence future export performance:
- Global Economic Growth: The pace of global economic growth will be a key determinant of U.S. export volumes. A stronger global economy will lead to increased demand for U.S. products.
- Inflation and Interest Rates: The trajectory of inflation and interest rates in the U.S. and other countries will impact production costs and consumer spending, which in turn will affect export demand.
- Geopolitical Developments: Geopolitical events and trade tensions will continue to pose risks to U.S. exports.
- Technological Innovation: Technological innovation and shifts in consumer preferences will create new export opportunities and challenges.
Conclusion
The decline in U.S. exports in Q2 2023 is a cause for concern, but it is not necessarily indicative of a long-term trend. The U.S. economy has the potential to rebound and regain its export momentum. By addressing the underlying factors contributing to the decline, implementing appropriate policy responses, and adapting to changing global conditions, the U.S. can promote future export growth and maintain its position as a leading trading nation.