“NASA’s Center for Near-Earth Object Studies Issues New Findings
Related Articles NASA’s Center for Near-Earth Object Studies Issues New Findings
- U.S. Government Opens Additional Acreage In Alaska For Drilling
- Greenland Rejects Trump’s Claim Amid Diplomatic Friction
- Colossal Biosciences Creates “Woolly Mouse” With Mammoth Traits, Paving The Way For De-Extinction
- Trump Accuses Ukraine Of Initiating War, Calls For New Elections
- Europe Steps Up Military Aid To Ukraine As U.S. Pulls Back
Introduction
With great enthusiasm, let’s explore interesting topics related to NASA’s Center for Near-Earth Object Studies Issues New Findings. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
NASA’s Center for Near-Earth Object Studies Issues New Findings
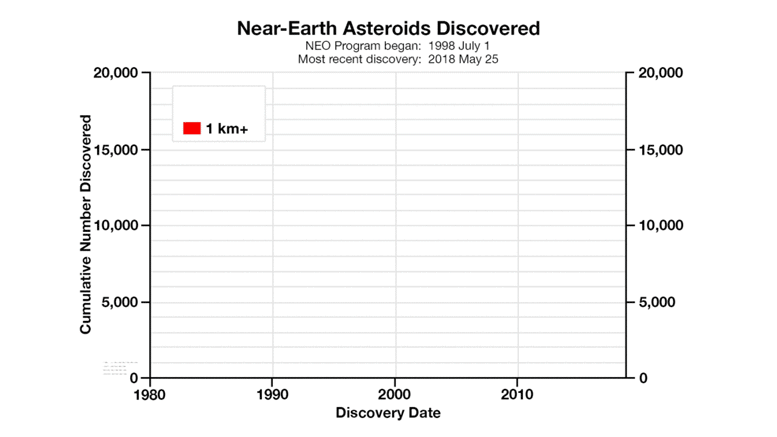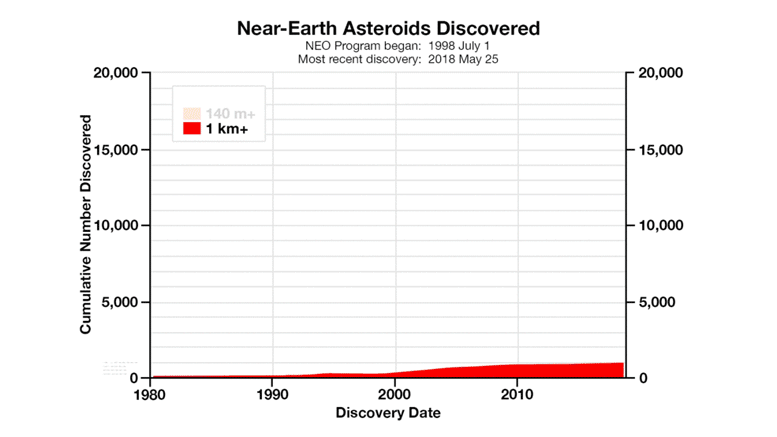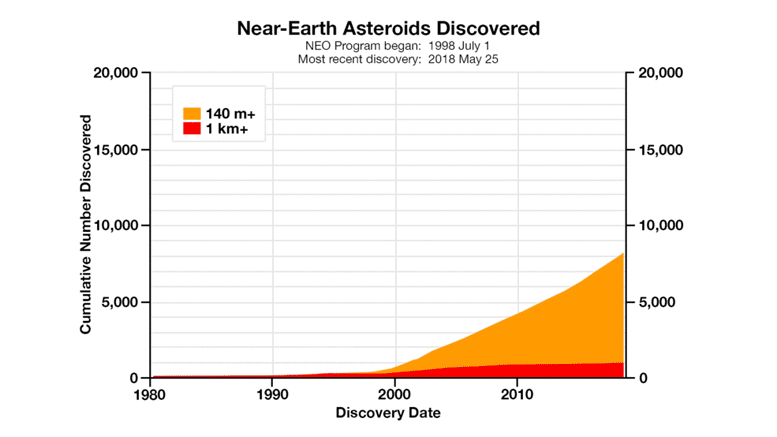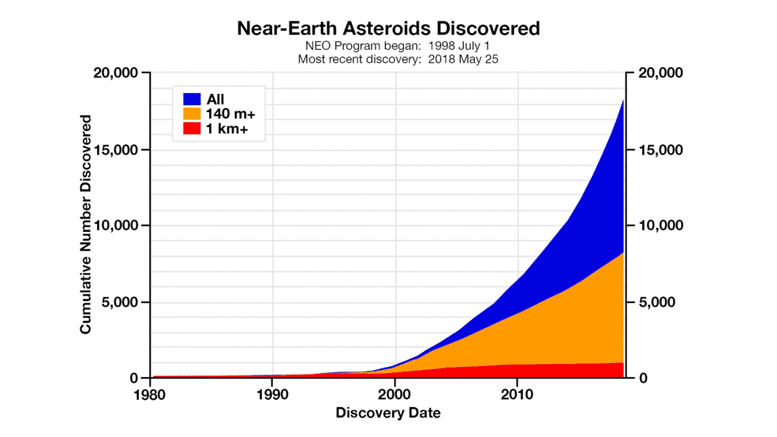
The Center for Near-Earth Object Studies (CNEOS) at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) plays a crucial role in monitoring and characterizing near-Earth objects (NEOs) that could potentially pose a threat to our planet. NEOs include asteroids and comets whose orbits bring them within a certain distance of Earth’s orbit. CNEOS uses observations and data from ground-based telescopes, space-based observatories, and radar systems to determine the orbits, sizes, and compositions of these objects. By studying NEOs, scientists can better understand the potential risks they pose and develop strategies to mitigate those risks.
Recently, CNEOS has released a series of new findings that have expanded our understanding of NEOs and their potential impact on Earth. These findings are based on a combination of new observations, improved data analysis techniques, and advanced computer modeling.
New Discoveries and Observations
One of the most significant findings from CNEOS is the discovery of several new NEOs that had previously gone undetected. These new discoveries have been made possible by the development of more sensitive telescopes and more sophisticated search algorithms. CNEOS scientists use these tools to scan the skies for faint or rapidly moving objects that could be NEOs.
In addition to discovering new NEOs, CNEOS has also made new observations of previously known NEOs. These observations have allowed scientists to refine the orbits of these objects and better predict their future trajectories. By tracking the movements of NEOs over time, scientists can identify any that may be on a collision course with Earth.
Improved Data Analysis Techniques
Another important factor contributing to CNEOS’s new findings is the development of improved data analysis techniques. CNEOS scientists use these techniques to extract more information from the available observations of NEOs. For example, they can use radar data to determine the size, shape, and rotation rate of an asteroid. They can also use spectroscopic data to determine the composition of an asteroid’s surface.
By combining data from different sources and using advanced analysis techniques, CNEOS scientists can develop more accurate models of NEOs and their orbits. These models are essential for predicting the potential impact of an NEO on Earth.
Advanced Computer Modeling
CNEOS also relies on advanced computer modeling to simulate the behavior of NEOs and assess their potential impact risks. These models take into account a variety of factors, including the size, shape, composition, and orbit of an NEO, as well as the gravitational effects of the Sun, Earth, and other planets.
By running these simulations, CNEOS scientists can estimate the probability that an NEO will collide with Earth and the potential consequences of such a collision. These simulations can also help to identify the most effective strategies for mitigating the risks posed by NEOs.
Specific Findings and Implications
Here are some specific findings from CNEOS and their implications:
-
Increased Number of Known NEOs: CNEOS has significantly increased the number of known NEOs. This increase is due to improved observational capabilities and data analysis techniques. With more NEOs identified, scientists have a better understanding of the overall population of these objects and their potential impact risks.
- Implication: A larger sample size allows for more accurate statistical analysis of NEO populations, helping to refine risk assessments and inform mitigation strategies.
-
Refined Orbit Determinations: CNEOS has refined the orbit determinations of many known NEOs. This refinement is based on new observations and improved data analysis techniques. More accurate orbit determinations allow scientists to better predict the future trajectories of NEOs and identify any that may be on a collision course with Earth.
- Implication: More precise orbit predictions reduce uncertainties in long-term impact assessments, enabling better preparation and resource allocation for potential mitigation efforts.
-
Characterization of NEO Properties: CNEOS has characterized the properties of many NEOs, including their size, shape, composition, and rotation rate. This characterization is based on radar data, spectroscopic data, and other types of observations. Knowing the properties of NEOs is essential for understanding their potential impact risks and developing strategies to mitigate those risks.
- Implication: Understanding an NEO’s physical properties is crucial for assessing its potential impact energy and designing effective deflection or disruption strategies.
-
Impact Risk Assessments: CNEOS has conducted impact risk assessments for many NEOs. These assessments take into account the size, shape, composition, and orbit of an NEO, as well as the gravitational effects of the Sun, Earth, and other planets. The results of these assessments are used to prioritize NEOs for further study and to develop strategies for mitigating the risks they pose.
- Implication: Prioritizing NEOs based on impact risk allows for focused research and resource allocation, ensuring that the most potentially hazardous objects receive the most attention.
-
Discovery of Potentially Hazardous Asteroids (PHAs): CNEOS has identified several new Potentially Hazardous Asteroids (PHAs). PHAs are NEOs that have the potential to make close approaches to Earth and are large enough to cause significant damage if they were to impact our planet.
- Implication: The discovery of new PHAs underscores the importance of continued NEO surveys and monitoring efforts to identify and characterize potential threats.
Addressing Concerns and Misconceptions
It is important to address some common concerns and misconceptions about NEOs and their potential impact on Earth:
- The threat of an asteroid impact is not imminent: While there is always a small chance that an asteroid could impact Earth, the vast majority of NEOs do not pose a significant threat. CNEOS carefully monitors all known NEOs and assesses their potential impact risks.
- Scientists are working to mitigate the risks posed by NEOs: CNEOS and other organizations are actively working to develop strategies for mitigating the risks posed by NEOs. These strategies include deflecting asteroids from their collision course with Earth and disrupting asteroids into smaller, less harmful fragments.
- Public awareness and support are essential: Public awareness and support are essential for ensuring that resources are available to continue monitoring NEOs and developing mitigation strategies.
Future Directions
CNEOS is continuing to improve its capabilities for detecting, tracking, and characterizing NEOs. Future directions for CNEOS include:
- Developing more sensitive telescopes: More sensitive telescopes will allow CNEOS to detect fainter and more distant NEOs.
- Improving data analysis techniques: Improved data analysis techniques will allow CNEOS to extract more information from the available observations of NEOs.
- Developing more advanced computer models: More advanced computer models will allow CNEOS to simulate the behavior of NEOs more accurately and assess their potential impact risks more effectively.
- Collaborating with international partners: Collaboration with international partners will allow CNEOS to share data and expertise and to coordinate efforts to monitor and mitigate the risks posed by NEOs.
Conclusion
NASA’s Center for Near-Earth Object Studies is playing a vital role in protecting our planet from the potential threat of asteroid impacts. The new findings from CNEOS are expanding our understanding of NEOs and their potential impact on Earth. By continuing to monitor NEOs and develop mitigation strategies, CNEOS is helping to ensure the safety and security of our planet. The ongoing efforts of CNEOS and other organizations are crucial for understanding and mitigating the risks posed by NEOs, ensuring the long-term safety of our planet. With continued advancements in technology and international collaboration, we can further enhance our ability to detect, track, and characterize NEOs, reducing the uncertainties in impact assessments and improving our preparedness for potential threats.