“Federal Reserve Interest Rates: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles Federal Reserve Interest Rates: A Comprehensive Overview
- The Ultimate Guide to Vulnerability Management: Protecting Your Systems and Data
- Supreme Court Overturns Roe V. Wade, Ending Constitutional Right To Abortion
- The Comprehensive Guide to the Security Operations Center in Cybersecurity
- The World Liberty Financial Scandal: A House Of Cards Built On Dreams
- Biden’s Approval Rating In May 2025: A Mid-Term Assessment And Future Projections
Introduction
We will be happy to explore interesting topics related to Federal Reserve Interest Rates: A Comprehensive Overview. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Federal Reserve Interest Rates: A Comprehensive Overview
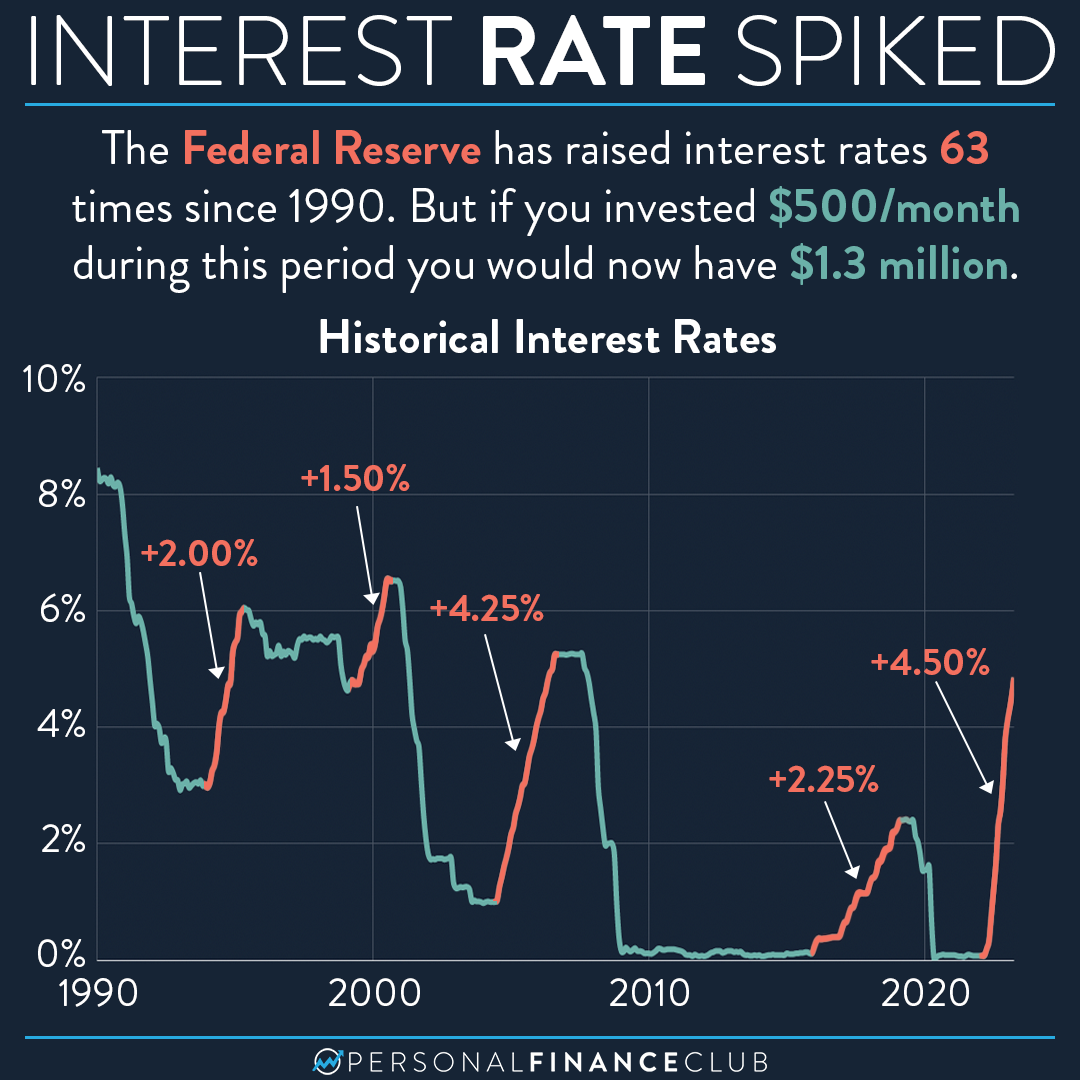
The Federal Reserve (also known as the Fed) is the central bank of the United States. It is responsible for overseeing the country’s monetary policy, which includes setting interest rates. The Fed’s interest rate decisions have a significant impact on the economy, influencing everything from inflation and unemployment to economic growth and investment. Understanding these rates is crucial for businesses, investors, and anyone interested in the financial health of the nation.
What are Federal Reserve Interest Rates?
The Federal Reserve influences the economy through several key interest rates, including:
-
Federal Funds Rate: This is the target rate that the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) sets for overnight lending between banks. Banks lend reserves to each other to meet reserve requirements set by the Fed. The federal funds rate serves as a benchmark for other short-term interest rates.
-
Discount Rate: This is the interest rate at which commercial banks can borrow money directly from the Fed. The discount rate is typically set higher than the federal funds rate to encourage banks to borrow from each other.
-
Interest on Reserve Balances (IORB): This is the interest rate the Fed pays to banks on the reserves they hold at the Fed. IORB helps to set a floor for the federal funds rate, as banks have less incentive to lend reserves at a rate below what they can earn from the Fed.
-
Overnight Reverse Repurchase Agreement (ON RRP) Rate: This is the rate at which the Fed offers overnight reverse repurchase agreements to eligible counterparties. It serves as a supplementary tool to help control the federal funds rate.
How the Fed Sets Interest Rates
The FOMC, which consists of the Board of Governors and five Reserve Bank presidents, meets eight times a year to assess the state of the economy and decide on monetary policy. The FOMC considers a wide range of economic indicators, including:
- Inflation: The Fed aims to maintain price stability, typically targeting an inflation rate of 2%.
- Employment: The Fed seeks to promote maximum employment, considering factors such as the unemployment rate, job growth, and labor force participation.
- Economic Growth: The Fed monitors indicators such as GDP growth, consumer spending, and business investment to assess the overall health of the economy.
- Financial Market Conditions: The Fed also considers conditions in financial markets, including stock prices, bond yields, and credit spreads.
Based on its assessment of these factors, the FOMC decides whether to raise, lower, or hold steady the federal funds rate. These decisions are not taken lightly, as they have far-reaching consequences for the economy.
The Impact of Interest Rate Changes
Changes in the Federal Reserve’s interest rates have a ripple effect throughout the economy. Here are some of the key impacts:
-
Borrowing Costs: When the Fed raises interest rates, it becomes more expensive for businesses and consumers to borrow money. This can lead to a decrease in investment and spending, which can slow down economic growth. Conversely, when the Fed lowers interest rates, borrowing becomes cheaper, which can stimulate economic activity.
-
Inflation: Higher interest rates can help to curb inflation by reducing demand in the economy. As borrowing costs rise, consumers and businesses tend to spend less, which can ease inflationary pressures. Lower interest rates can have the opposite effect, potentially leading to higher inflation if demand outpaces supply.
-
Savings and Investments: Interest rate changes also affect savings and investments. Higher interest rates can make saving more attractive, as people can earn more on their deposits. Lower interest rates can encourage investors to seek higher-yielding assets, such as stocks or real estate.
-
Exchange Rates: Interest rate differentials between countries can influence exchange rates. When the Fed raises interest rates, it can make the U.S. dollar more attractive to foreign investors, leading to an appreciation of the dollar. A stronger dollar can make U.S. exports more expensive and imports cheaper.
-
Housing Market: Interest rates play a crucial role in the housing market. Lower interest rates can make mortgages more affordable, boosting demand for homes and driving up prices. Higher interest rates can have the opposite effect, cooling down the housing market.
-
Job Market: The Fed’s interest rate decisions can also impact the job market. Lower interest rates can stimulate economic growth, leading to increased hiring and lower unemployment. Higher interest rates can slow down economic activity, potentially leading to job losses.
Recent Trends and Future Outlook
In recent years, the Federal Reserve has navigated a complex economic landscape, marked by factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic, supply chain disruptions, and rising inflation. In response to the pandemic, the Fed lowered interest rates to near zero and implemented various other measures to support the economy.
However, as the economy recovered and inflation surged, the Fed began to raise interest rates aggressively in 2022 and 2023. The goal was to bring inflation back down to its 2% target. As of late 2023, the Fed has paused rate hikes, signaling a potential shift in monetary policy.
Looking ahead, the Fed’s interest rate decisions will continue to be guided by its dual mandate of price stability and maximum employment. The path of interest rates will depend on how the economy evolves and how the Fed assesses the balance of risks.
Criticisms and Debates
The Federal Reserve’s interest rate policies are not without their critics. Some argue that the Fed’s actions can have unintended consequences and that it is difficult to predict the full impact of interest rate changes. Others argue that the Fed should focus more on one objective, such as price stability, rather than trying to balance multiple goals.
There are also debates about the appropriate level of interest rates. Some economists believe that the Fed should keep interest rates low to stimulate economic growth, while others argue that low interest rates can lead to asset bubbles and financial instability.
Conclusion
Federal Reserve interest rates are a powerful tool that can influence the economy in many ways. Understanding how the Fed sets interest rates and the impact of these decisions is essential for businesses, investors, and anyone interested in the financial health of the nation. While there are debates about the appropriate level of interest rates and the Fed’s role in the economy, there is no doubt that the Fed’s actions have a significant impact on our lives. As the economy continues to evolve, the Fed’s interest rate policies will continue to be a subject of intense scrutiny and debate.