“Solar Power Incentives: Driving the Global Transition to Renewable Energy
Related Articles Solar Power Incentives: Driving the Global Transition to Renewable Energy
- The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Security Event Management
- Ultimate Security Incident Response Guide for Bulletproof Cyber Defenses
- The Ultimate Guide to Threat Response Frameworks for Enhanced Cybersecurity
- X (Twitter) Faces Mounting Legal Challenges Over Misinformation: A Deep Dive
- Secure Your Digital Realm: Enhanced Threat Detection Solutions
Introduction
We will be happy to explore interesting topics related to Solar Power Incentives: Driving the Global Transition to Renewable Energy. Let’s knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Solar Power Incentives: Driving the Global Transition to Renewable Energy
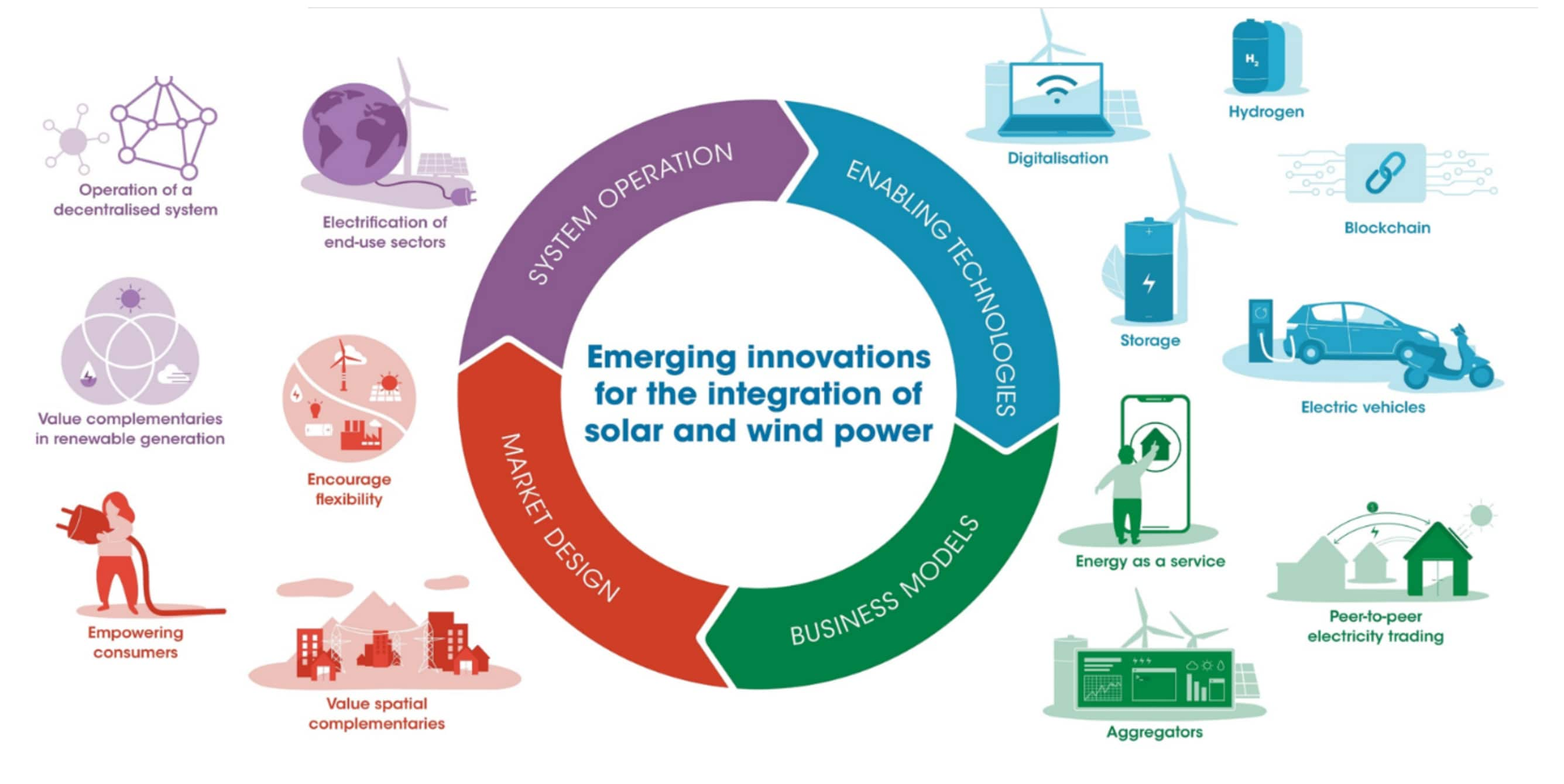
Introduction
In the face of escalating climate change concerns and the urgent need for sustainable energy sources, solar power has emerged as a frontrunner in the global transition to renewable energy. Solar power incentives play a pivotal role in accelerating the adoption of solar technology by reducing the financial barriers and making it more accessible to individuals, businesses, and communities. These incentives take various forms, including tax credits, rebates, grants, feed-in tariffs, and net metering policies. This article explores the significance of solar power incentives, their types, benefits, challenges, and their overall impact on driving the global transition to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
The Significance of Solar Power Incentives
Solar power incentives are designed to address the high upfront costs associated with installing solar energy systems. These incentives serve as financial catalysts, encouraging individuals, businesses, and organizations to invest in solar technology by lowering the initial investment required. By reducing the financial burden, solar power incentives make solar energy more economically viable and attractive, thus promoting its widespread adoption.
Types of Solar Power Incentives
Solar power incentives come in various forms, each with its own unique mechanism and impact. Here are some of the most common types of solar power incentives:
-
Tax Credits: Tax credits are a popular form of solar power incentive that allows individuals and businesses to deduct a percentage of the cost of their solar energy system from their federal or state income taxes. Tax credits can significantly reduce the overall cost of solar installation, making it more affordable for a wider range of consumers.
-
Rebates: Rebates are direct financial incentives provided by state governments, local municipalities, or utility companies to individuals and businesses that install solar energy systems. Rebates can be offered as a fixed amount or as a percentage of the total system cost. They provide an immediate financial benefit, making solar energy more attractive to potential adopters.
-
Grants: Grants are financial awards provided by government agencies, non-profit organizations, or private foundations to support solar energy projects. Grants are typically awarded based on specific criteria, such as project size, location, or community impact. They can be used to fund solar installations for homes, businesses, schools, and other organizations.
-
Feed-in Tariffs (FITs): Feed-in tariffs are policies that require utility companies to purchase excess electricity generated by solar energy systems at a predetermined rate. FITs provide solar energy producers with a guaranteed revenue stream, making solar energy investments more financially secure. They encourage individuals and businesses to install solar panels and sell excess electricity back to the grid.
-
Net Metering: Net metering is a billing mechanism that allows solar energy producers to receive credit for excess electricity they send back to the grid. Under net metering policies, solar energy producers are only charged for the net amount of electricity they consume from the grid, which is the difference between the electricity they use and the electricity they generate. Net metering encourages solar energy adoption by allowing consumers to offset their electricity bills and potentially earn credits for excess generation.
Benefits of Solar Power Incentives
Solar power incentives offer a wide range of benefits, including:
-
Reduced Energy Costs: Solar power incentives help lower the upfront costs of solar energy systems, making them more affordable for individuals, businesses, and organizations. By reducing the financial barrier, solar power incentives enable more people to access clean and affordable solar energy, which can significantly lower their monthly energy bills.
-
Environmental Benefits: Solar power incentives promote the adoption of solar energy, which is a clean and renewable energy source. Solar energy does not produce greenhouse gas emissions or air pollutants, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, solar power incentives help mitigate climate change and improve air quality.
-
Economic Growth: Solar power incentives stimulate economic growth by creating jobs in the solar industry. The installation, maintenance, and manufacturing of solar energy systems require a skilled workforce, which can lead to job creation and economic development. Solar power incentives also attract investment in the solar industry, further boosting economic growth.
-
Energy Independence: Solar power incentives promote energy independence by reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels. By generating electricity from domestic solar resources, countries can reduce their dependence on foreign energy sources and enhance their energy security. Solar power incentives also encourage the development of local solar industries, further strengthening energy independence.
-
Grid Stability: Solar power incentives can enhance grid stability by diversifying the energy mix and reducing reliance on centralized power plants. Distributed solar energy systems can provide electricity closer to where it is needed, reducing transmission losses and improving grid resilience. Solar power incentives also encourage the development of smart grid technologies, which can further enhance grid stability.
Challenges of Solar Power Incentives
While solar power incentives offer numerous benefits, they also face certain challenges:
-
Cost: Solar power incentives can be expensive, particularly for large-scale projects. Governments and utility companies need to carefully consider the costs and benefits of different incentive programs to ensure that they are cost-effective and sustainable.
-
Complexity: Solar power incentive programs can be complex and difficult to navigate, particularly for individuals and small businesses. Simplifying the application process and providing clear and concise information can help improve participation rates.
-
Equity: Solar power incentives may not be equally accessible to all segments of the population. Low-income households and communities may face barriers to accessing solar energy, even with incentives in place. Targeted programs and outreach efforts are needed to ensure that solar power incentives benefit all members of society.
-
Sustainability: Solar power incentive programs need to be designed to be sustainable over the long term. Short-term incentives can create uncertainty and discourage investment in the solar industry. Long-term, predictable incentives are needed to create a stable market for solar energy.
-
Grid Integration: The integration of solar energy into the grid can pose challenges, particularly in areas with high solar penetration. Grid operators need to develop new technologies and strategies to manage the variability of solar energy and ensure grid stability.
The Impact of Solar Power Incentives on the Global Transition to Renewable Energy
Solar power incentives have played a crucial role in driving the global transition to renewable energy. By reducing the financial barriers to solar energy adoption, these incentives have enabled more individuals, businesses, and organizations to invest in solar technology. As a result, solar energy capacity has grown exponentially in recent years, making it one of the fastest-growing renewable energy sources in the world.
Solar power incentives have also helped to create a thriving solar industry, which has generated jobs and economic growth. The solar industry is now a major employer in many countries, and it is expected to continue to grow as solar energy becomes more affordable and accessible.
Furthermore, solar power incentives have helped to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality. By displacing fossil fuels, solar energy has reduced the amount of carbon dioxide and other pollutants released into the atmosphere. This has helped to mitigate climate change and improve public health.
Conclusion
Solar power incentives are essential for driving the global transition to renewable energy. By reducing the financial barriers to solar energy adoption, these incentives have enabled more individuals, businesses, and organizations to invest in solar technology. As a result, solar energy capacity has grown exponentially, creating jobs, stimulating economic growth, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. While solar power incentives face certain challenges, their benefits far outweigh their costs. By carefully designing and implementing solar power incentive programs, governments and utility companies can accelerate the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
