“Auto Industry Lobbies Against EV Tariffs
Related Articles Auto Industry Lobbies Against EV Tariffs
- Retail Sales Rise Unexpectedly In May, Signaling Economic Resilience
- The Ultimate Guide to Threat Detection: Protect Your Cybersecurity
- Mexican Independence Day: A Vibrant Celebration Of Freedom And Heritage
- Headline: "CogniSense Unveiled: Revolutionizing Decision-Making With AI-Powered Intuition"
- Master the Art of Advanced Threat Protection: Your Cybersecurity Fortress
Introduction
With great enthusiasm, let’s explore interesting topics related to Auto Industry Lobbies Against EV Tariffs. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Auto Industry Lobbies Against EV Tariffs
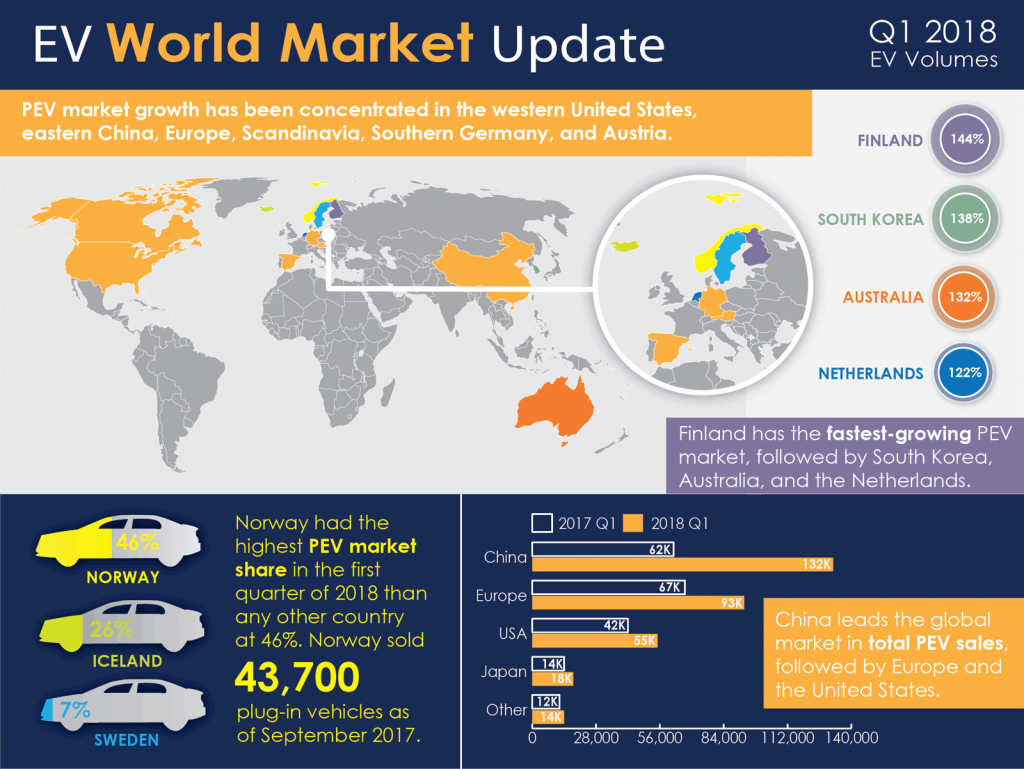
The automotive industry is a powerful force in the global economy, with a significant impact on employment, trade, and technological innovation. As the world increasingly focuses on sustainable transportation, electric vehicles (EVs) have emerged as a promising solution to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. However, the transition to EVs is not without its challenges, and one of the most contentious issues is the imposition of tariffs on EVs.
Tariffs are taxes imposed on imported goods, and they can have a significant impact on the price and competitiveness of EVs. While some argue that tariffs are necessary to protect domestic industries and promote local production, others contend that they hinder the adoption of EVs, stifle innovation, and harm consumers. The automotive industry is deeply divided on this issue, with various stakeholders engaging in intense lobbying efforts to influence government policies on EV tariffs.
Arguments for EV Tariffs
Proponents of EV tariffs argue that they are essential for safeguarding domestic automotive industries and ensuring a level playing field. They claim that tariffs can:
- Protect Domestic Jobs: Tariffs can make imported EVs more expensive, thereby increasing the demand for domestically produced EVs. This can help protect jobs in the domestic automotive industry and prevent job losses due to foreign competition.
- Promote Local Production: Tariffs can incentivize automakers to establish or expand EV production facilities within the country. This can create new jobs, stimulate economic growth, and reduce reliance on foreign suppliers.
- Counter Unfair Trade Practices: Tariffs can be used as a tool to counter unfair trade practices by foreign countries, such as subsidies or intellectual property theft. This can help level the playing field and ensure that domestic automakers can compete fairly.
- National Security: In some cases, tariffs may be justified on national security grounds. For example, tariffs on EV batteries could be imposed to ensure a reliable supply of batteries for critical applications, such as military vehicles.
Arguments Against EV Tariffs
Opponents of EV tariffs argue that they are detrimental to the adoption of EVs, stifle innovation, and harm consumers. They claim that tariffs can:
- Increase EV Prices: Tariffs make imported EVs more expensive, which can deter consumers from purchasing them. This can slow down the adoption of EVs and hinder efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Limit Consumer Choice: Tariffs reduce the availability of EV models in the market, limiting consumer choice and potentially forcing them to purchase less desirable or more expensive EVs.
- Stifle Innovation: Tariffs can reduce competition among EV manufacturers, which can stifle innovation and slow down the development of new and improved EV technologies.
- Harm Consumers: Tariffs ultimately harm consumers by increasing the price of EVs and limiting their choices. This can make it more difficult for consumers to switch to EVs and enjoy the benefits of cleaner transportation.
- Hurt International Trade: Tariffs can spark retaliatory measures from other countries, leading to trade wars and harming international trade. This can disrupt global supply chains and make it more difficult for automakers to operate efficiently.
Lobbying Efforts by the Auto Industry
The automotive industry is actively engaged in lobbying efforts to influence government policies on EV tariffs. Automakers, industry associations, and other stakeholders spend millions of dollars each year lobbying policymakers to support their respective positions on tariffs.
- Automakers: Automakers are among the most influential lobbyists on EV tariffs. Some automakers support tariffs to protect their domestic production, while others oppose them to maintain access to global markets. For example, General Motors and Ford have historically supported tariffs on imported vehicles, while Tesla has opposed them.
- Industry Associations: Industry associations, such as the Alliance for Automotive Innovation and the European Automobile Manufacturers Association (ACEA), also play a significant role in lobbying on EV tariffs. These associations represent the interests of their member companies and advocate for policies that support the automotive industry as a whole.
- Other Stakeholders: Other stakeholders, such as labor unions, environmental groups, and consumer advocacy organizations, also engage in lobbying on EV tariffs. These groups have diverse interests and may support or oppose tariffs depending on their specific goals.
Examples of Lobbying Efforts
Here are some examples of lobbying efforts by the auto industry on EV tariffs:
- In 2018, the Trump administration imposed tariffs on imported steel and aluminum, which increased the cost of manufacturing vehicles in the United States. The Alliance for Automotive Innovation lobbied against these tariffs, arguing that they would harm the competitiveness of the US auto industry.
- In 2021, the European Commission proposed a carbon border adjustment mechanism (CBAM), which would impose a carbon tax on imported goods based on their carbon content. ACEA lobbied against the CBAM, arguing that it would penalize European automakers and harm the competitiveness of the European auto industry.
- In 2022, the US Inflation Reduction Act included tax credits for EVs, but these credits were limited to EVs assembled in North America. Several foreign automakers lobbied against this provision, arguing that it discriminated against foreign-made EVs.
The Impact of Lobbying
Lobbying can have a significant impact on government policies on EV tariffs. Policymakers often rely on information and expertise provided by lobbyists to make informed decisions. Lobbying can also influence public opinion and shape the political debate on EV tariffs.
The effectiveness of lobbying depends on several factors, including the resources and influence of the lobbyists, the political climate, and the specific issue at stake. Lobbying is more likely to be successful when it is supported by a broad coalition of stakeholders and when it aligns with the prevailing political winds.
Conclusion
The issue of EV tariffs is complex and contentious, with strong arguments on both sides. The automotive industry is deeply divided on this issue, with various stakeholders engaging in intense lobbying efforts to influence government policies.
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to impose EV tariffs will depend on a variety of factors, including economic considerations, political pressures, and national security concerns. Policymakers must carefully weigh the potential benefits and drawbacks of tariffs before making a decision.
The lobbying efforts of the auto industry will undoubtedly play a significant role in shaping the debate on EV tariffs and influencing the final outcome. It is important for policymakers to consider all perspectives and make decisions that are in the best interests of the economy, the environment, and consumers.
The future of EVs and the transition to sustainable transportation depend on sound policies that promote innovation, competition, and consumer choice. Tariffs can play a role in this transition, but they must be carefully considered and implemented in a way that does not harm the long-term interests of the automotive industry and the global economy.
