“COVID-19 Vaccine Updates: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles COVID-19 Vaccine Updates: A Comprehensive Overview
- Canada Border Trade: A Vital Economic Lifeline
- Cutting-Edge Threat Detection Systems for Enhanced Cyber Security
- Latin American Migration Policy: A Complex Tapestry Of Shifting Priorities
- Donald Trump $TRUMP Token: A Wild Ride Through Meme Coin Mania And Political Speculation
- H1B Visa Cap News: Understanding The Challenges And Potential Reforms
Introduction
With great enthusiasm, let’s explore interesting topics related to COVID-19 Vaccine Updates: A Comprehensive Overview. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
COVID-19 Vaccine Updates: A Comprehensive Overview
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on global health, economies, and societies. Vaccines have emerged as a critical tool in combating the virus, reducing severe illness, hospitalization, and death. Since the initial rollout of COVID-19 vaccines, there have been numerous updates and developments. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of COVID-19 vaccines, including the types of vaccines available, their efficacy, safety, booster recommendations, and ongoing research.
Types of COVID-19 Vaccines
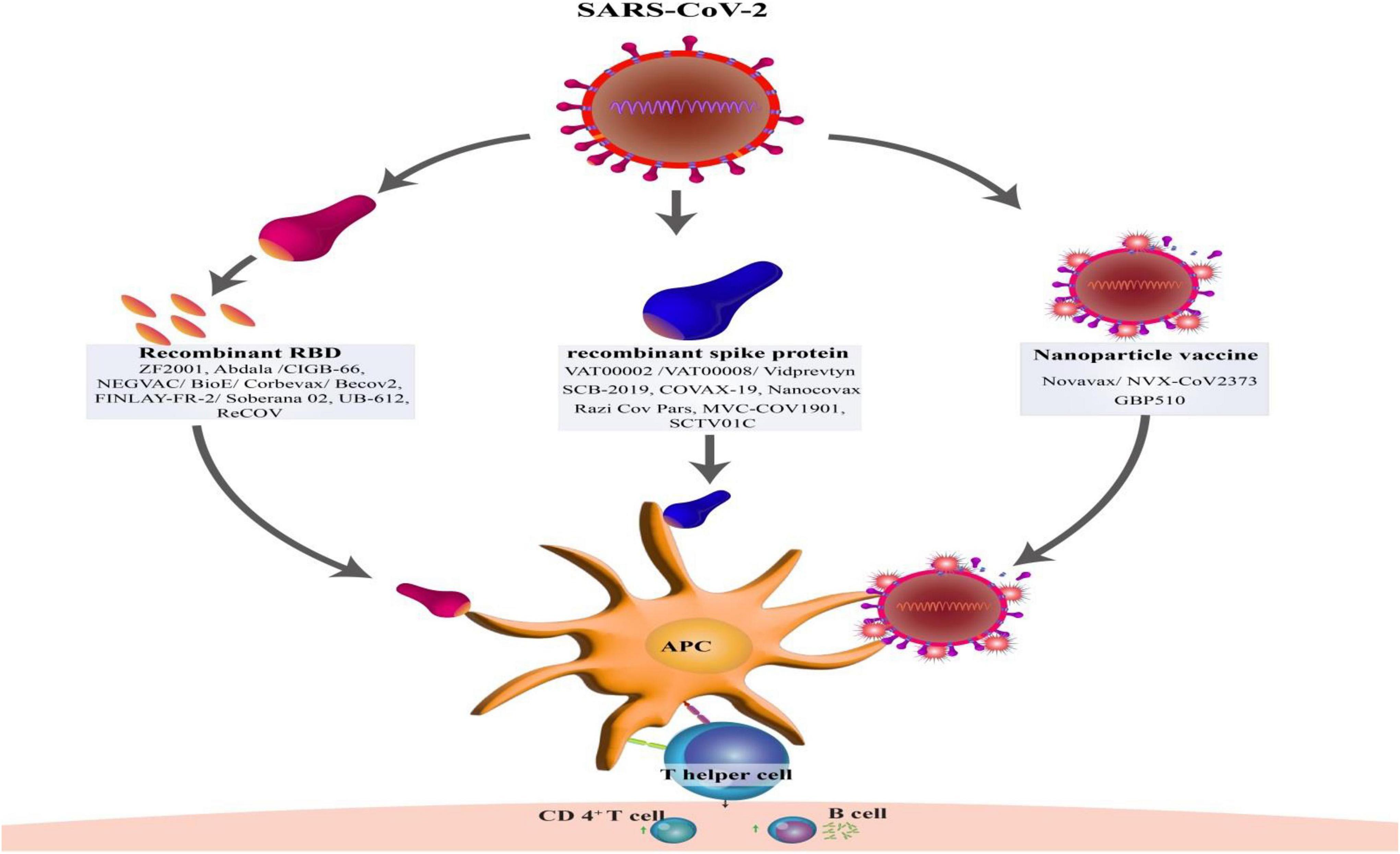
Several types of COVID-19 vaccines have been developed and authorized for use worldwide. These vaccines utilize different technologies to stimulate an immune response against the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The main types of COVID-19 vaccines include:
-
mRNA Vaccines: These vaccines, developed by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna, use messenger RNA (mRNA) to instruct cells to produce a harmless piece of the viral spike protein. This triggers an immune response, preparing the body to fight off the virus if exposed. mRNA vaccines have demonstrated high efficacy and have been widely used globally.
-
Viral Vector Vaccines: Vaccines like those from Johnson & Johnson/Janssen and AstraZeneca-Oxford use a modified version of a different virus (adenovirus) to deliver genetic material from the SARS-CoV-2 virus into cells. This prompts an immune response, similar to mRNA vaccines. Viral vector vaccines have also shown good efficacy and have been used in many countries.
-
Protein Subunit Vaccines: Novavax is a protein subunit vaccine that contains fragments of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. When injected, these protein fragments stimulate the immune system to produce antibodies and immune cells that target the virus. Protein subunit vaccines are well-established and have a good safety profile.
-
Inactivated Virus Vaccines: These vaccines, such as those developed by Sinopharm and Sinovac, use an inactivated or weakened form of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The inactivated virus cannot cause infection but still triggers an immune response. Inactivated virus vaccines have been used extensively, particularly in China and other parts of the world.
Efficacy of COVID-19 Vaccines
The efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines has been extensively studied in clinical trials and real-world settings. Overall, the vaccines have demonstrated high efficacy in preventing symptomatic COVID-19, severe illness, hospitalization, and death.
-
mRNA Vaccines: Clinical trials have shown that the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines have efficacy rates of around 95% in preventing symptomatic COVID-19. Real-world data has also confirmed their high effectiveness in reducing severe outcomes.
-
Viral Vector Vaccines: The Johnson & Johnson/Janssen vaccine has shown an efficacy of around 66% in preventing moderate to severe COVID-19. The AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccine has demonstrated varying efficacy rates depending on the dosing regimen, with some studies showing efficacy of up to 80%.
-
Protein Subunit Vaccines: The Novavax vaccine has shown an efficacy of around 90% in clinical trials, making it a highly effective option for preventing symptomatic COVID-19.
-
Inactivated Virus Vaccines: The efficacy of inactivated virus vaccines varies, with some studies showing efficacy rates of around 50-80% in preventing symptomatic COVID-19.
It’s important to note that vaccine efficacy can vary depending on factors such as the variant of the virus, the age and health status of the individual, and the time since vaccination.
Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines
COVID-19 vaccines have undergone rigorous safety testing in clinical trials and have been closely monitored since their rollout. Overall, the vaccines have been found to be safe and well-tolerated.
Common side effects of COVID-19 vaccines include:
- Pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Fever
- Chills
- Nausea
These side effects are usually mild to moderate and resolve within a few days.
Rare but serious side effects have been reported with some COVID-19 vaccines. These include:
-
Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (TTS): TTS is a rare condition involving blood clots and low platelet counts. It has been associated with the Johnson & Johnson/Janssen and AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccines. The risk of TTS is very low, and health authorities have provided guidance on how to recognize and treat it.
-
Myocarditis and Pericarditis: Myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle) and pericarditis (inflammation of the lining around the heart) have been reported as rare side effects, particularly after mRNA vaccines. The risk is highest in young men, but the condition is usually mild and resolves quickly.
-
Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS): GBS is a rare autoimmune disorder that can cause muscle weakness and paralysis. It has been associated with the Johnson & Johnson/Janssen vaccine.
Health authorities continuously monitor vaccine safety and provide updated guidance as needed. The benefits of COVID-19 vaccination far outweigh the risks of potential side effects.
Booster Recommendations
As the pandemic has evolved, and with the emergence of new variants, booster doses of COVID-19 vaccines have become an important strategy to maintain protection against the virus. Booster doses help to increase antibody levels and enhance the immune response, providing better protection against infection and severe illness.
Recommendations for booster doses vary by country and vaccine type. In general, booster doses are recommended for:
- Individuals who have completed their primary vaccination series (e.g., two doses of an mRNA vaccine or one dose of the Johnson & Johnson/Janssen vaccine)
- Individuals at higher risk of severe COVID-19, such as older adults, people with underlying medical conditions, and healthcare workers
Booster doses may be the same vaccine as the primary series or a different vaccine (heterologous boosting). Studies have shown that heterologous boosting can provide a broader and more robust immune response.
Health authorities regularly update booster recommendations based on the latest scientific evidence. It’s important to stay informed about the recommendations in your region and consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
COVID-19 Vaccines for Children
COVID-19 vaccines have been authorized for use in children, starting with adolescents and gradually expanding to younger age groups. Vaccinating children helps protect them from severe COVID-19, reduces the risk of transmission, and allows them to participate more safely in school and other activities.
The Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine has been authorized for use in children as young as 6 months old, while the Moderna vaccine has been authorized for children as young as 6 months old. The dosage and formulation of the vaccine may differ for children compared to adults.
Clinical trials have shown that COVID-19 vaccines are safe and effective in children. Side effects are generally mild and similar to those seen in adults.
Vaccinating children against COVID-19 is an important step in protecting the entire community and reducing the spread of the virus.
Ongoing Research
Research on COVID-19 vaccines is ongoing, with efforts focused on:
-
Developing vaccines that are more effective against new variants: As the virus evolves, new variants may emerge that are more resistant to existing vaccines. Researchers are working on developing updated vaccines that can provide better protection against these variants.
-
Developing vaccines that provide longer-lasting immunity: Current COVID-19 vaccines require booster doses to maintain protection. Researchers are exploring ways to develop vaccines that provide longer-lasting immunity, reducing the need for frequent boosters.
-
Developing vaccines that can prevent transmission: While current COVID-19 vaccines are effective at preventing severe illness, they are less effective at preventing transmission of the virus. Researchers are working on developing vaccines that can reduce or eliminate transmission, helping to control the spread of the virus.
-
Developing nasal vaccines: Nasal vaccines are administered through the nose and can stimulate an immune response directly in the respiratory tract, where the virus enters the body. Nasal vaccines may provide better protection against infection and transmission.
-
Understanding the long-term effects of COVID-19 vaccines: Researchers are studying the long-term effects of COVID-19 vaccines to ensure their continued safety and effectiveness.
Conclusion
COVID-19 vaccines have been a game-changer in the fight against the pandemic. They have demonstrated high efficacy in preventing severe illness, hospitalization, and death. While there have been updates and developments since the initial rollout, the vaccines remain a critical tool in protecting individuals and communities. Staying informed about the latest recommendations, booster doses, and ongoing research is essential for making informed decisions about vaccination. By continuing to vaccinate and follow public health guidelines, we can move closer to ending the pandemic and returning to a more normal way of life.