“Cybersecurity Breaches Expose Vulnerabilities: A Deep Dive into Risks, Impacts, and Mitigation Strategies
Related Articles Cybersecurity Breaches Expose Vulnerabilities: A Deep Dive into Risks, Impacts, and Mitigation Strategies
- Gun Safety Technology: A Comprehensive Overview
- Refugee Intake Numbers: Global Trends, National Policies, And Humanitarian Concerns
- Ultimate Guide to Cybersecurity Incident Handling for Optimal Cyber Resilience
- Rising Insurance Premiums: Understanding The Drivers And Navigating The Impact
- The Intricacies Of New York Rent Control Laws: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With great enthusiasm, let’s explore interesting topics related to Cybersecurity Breaches Expose Vulnerabilities: A Deep Dive into Risks, Impacts, and Mitigation Strategies. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Cybersecurity Breaches Expose Vulnerabilities: A Deep Dive into Risks, Impacts, and Mitigation Strategies
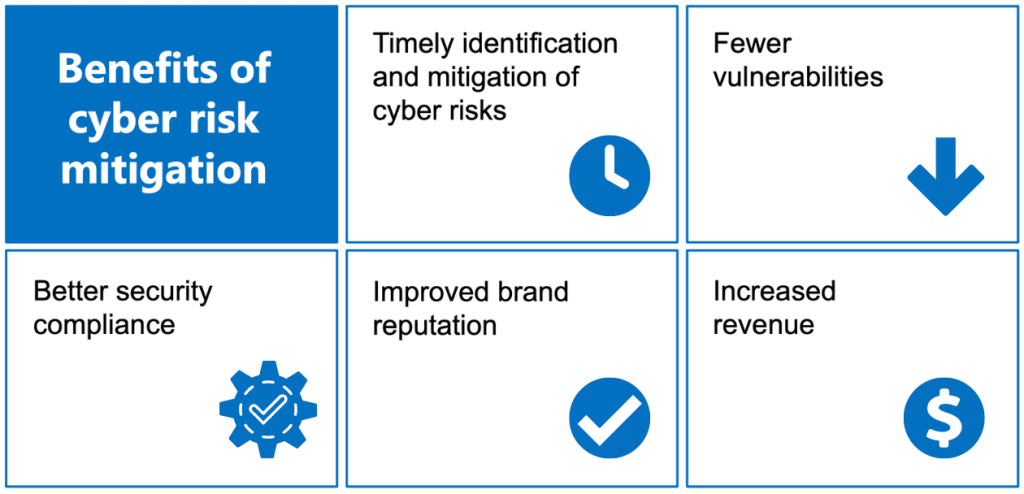
In an increasingly interconnected world, cybersecurity has become a critical concern for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. As technology advances, so do the sophistication and frequency of cyberattacks. Cybersecurity breaches, the unauthorized access to sensitive data or systems, have become a pervasive threat, exposing vulnerabilities that can have devastating consequences. This article delves into the multifaceted nature of cybersecurity breaches, examining the risks, impacts, and mitigation strategies necessary to protect against these evolving threats.
Understanding Cybersecurity Breaches
A cybersecurity breach occurs when an individual or group gains unauthorized access to a computer system, network, application, or data. These breaches can take many forms, including:
- Data breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive information, such as personal data, financial records, or intellectual property.
- Malware infections: Introduction of malicious software (malware) into a system, which can disrupt operations, steal data, or gain unauthorized control.
- Ransomware attacks: A type of malware that encrypts a victim’s data and demands a ransom payment for its release.
- Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks: Overwhelming a system or network with traffic, making it unavailable to legitimate users.
- Phishing attacks: Deceptive emails or websites that trick individuals into revealing sensitive information.
- Insider threats: Security breaches caused by employees, contractors, or other individuals with authorized access to systems or data.
Vulnerabilities Exposed by Cybersecurity Breaches
Cybersecurity breaches often expose underlying vulnerabilities in an organization’s security posture. These vulnerabilities can be technical, human, or organizational in nature. Some common vulnerabilities include:
- Software vulnerabilities: Flaws in software code that can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access or execute malicious code. These vulnerabilities are often due to programming errors, outdated software, or misconfigured systems.
- Weak passwords: Easily guessable or compromised passwords that allow attackers to gain access to accounts and systems.
- Lack of multi-factor authentication (MFA): The absence of an additional layer of security beyond a password, making it easier for attackers to gain access to accounts even if they have stolen or guessed the password.
- Social engineering: Exploiting human psychology to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security.
- Insider threats: Disgruntled or negligent employees who intentionally or unintentionally compromise security.
- Lack of security awareness: Insufficient training and awareness among employees about cybersecurity threats and best practices.
- Inadequate security policies and procedures: The absence of clear and comprehensive security policies and procedures to guide employee behavior and protect sensitive data.
- Insufficient monitoring and detection: The lack of robust monitoring and detection systems to identify and respond to security incidents in a timely manner.
- Poor data encryption: The failure to encrypt sensitive data, making it vulnerable to unauthorized access if a breach occurs.
- Cloud security misconfigurations: Improperly configured cloud services that leave data and systems vulnerable to attack.
Impacts of Cybersecurity Breaches
Cybersecurity breaches can have a wide range of negative impacts on individuals, organizations, and society as a whole. These impacts can include:
- Financial losses: Breaches can result in significant financial losses due to data theft, business disruption, legal fees, fines, and remediation costs.
- Reputational damage: A breach can damage an organization’s reputation, leading to loss of customer trust and business opportunities.
- Legal and regulatory consequences: Organizations that fail to protect sensitive data may face legal action and regulatory penalties.
- Identity theft: Stolen personal information can be used to commit identity theft, causing financial and emotional distress to victims.
- Business disruption: Breaches can disrupt business operations, leading to downtime, lost productivity, and customer service issues.
- Loss of intellectual property: Stolen intellectual property can give competitors an unfair advantage and undermine an organization’s competitive position.
- National security threats: Breaches targeting government agencies or critical infrastructure can pose a threat to national security.
- Erosion of trust: Cybersecurity breaches can erode trust in online services and digital technologies, hindering innovation and economic growth.
Mitigation Strategies
To protect against cybersecurity breaches and minimize their impact, organizations must implement a comprehensive security strategy that addresses technical, human, and organizational vulnerabilities. Key mitigation strategies include:
- Implement strong passwords and MFA: Enforce strong password policies and require MFA for all accounts.
- Patch software vulnerabilities: Regularly update software and apply security patches to address known vulnerabilities.
- Train employees on security awareness: Provide regular training to employees on cybersecurity threats, phishing attacks, and best practices.
- Develop and enforce security policies and procedures: Create clear and comprehensive security policies and procedures to guide employee behavior and protect sensitive data.
- Implement robust monitoring and detection systems: Deploy security information and event management (SIEM) systems and other monitoring tools to detect and respond to security incidents.
- Encrypt sensitive data: Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Secure cloud environments: Properly configure cloud services and implement security controls to protect data and systems in the cloud.
- Conduct regular security assessments and penetration testing: Identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in systems and networks through regular security assessments and penetration testing.
- Implement incident response plans: Develop and test incident response plans to effectively respond to and recover from security breaches.
- Share threat intelligence: Collaborate with other organizations and government agencies to share threat intelligence and stay informed about emerging threats.
- Use endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions: Implement EDR solutions to detect and respond to threats on individual devices.
- Employ a zero-trust security model: Implement a zero-trust security model, which assumes that no user or device is trusted by default and requires verification for every access request.
- Regularly back up data: Back up data regularly and store backups in a secure location to ensure that data can be recovered in the event of a breach.
- Implement data loss prevention (DLP) solutions: Use DLP solutions to prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control.
- Secure the supply chain: Assess the security posture of third-party vendors and suppliers to ensure that they are not a source of vulnerability.
The Importance of a Proactive Approach
In the face of evolving cybersecurity threats, a proactive approach to security is essential. Organizations must not only implement mitigation strategies but also continuously monitor and adapt their security posture to stay ahead of attackers. This requires a commitment to ongoing training, security assessments, and threat intelligence gathering.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity breaches are a significant threat to individuals, organizations, and society as a whole. By understanding the risks, impacts, and mitigation strategies associated with these breaches, organizations can take proactive steps to protect their data, systems, and reputation. A comprehensive security strategy that addresses technical, human, and organizational vulnerabilities is essential for mitigating the risk of cybersecurity breaches and minimizing their impact. As the threat landscape continues to evolve, organizations must remain vigilant and adapt their security posture to stay ahead of attackers and protect against emerging threats.
