“East Coast Swelters Under Oppressive Heat Wave
Related Articles East Coast Swelters Under Oppressive Heat Wave
- The Ultimate Guide to Endpoint Intrusion Response: Protect Your Network Today
- Empowering Real-time Monitoring for Enhanced Cyber Security
- Mastering Security Incident Handling: A Comprehensive Guide to Protect Your Cybersecurity
- Ripple Vs. SEC: A Landmark Ruling And Its Implications For The Crypto Industry
- All-Encompassing Endpoint Incident Response Strategies
Introduction
With great enthusiasm, let’s explore interesting topics related to East Coast Swelters Under Oppressive Heat Wave. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
East Coast Swelters Under Oppressive Heat Wave
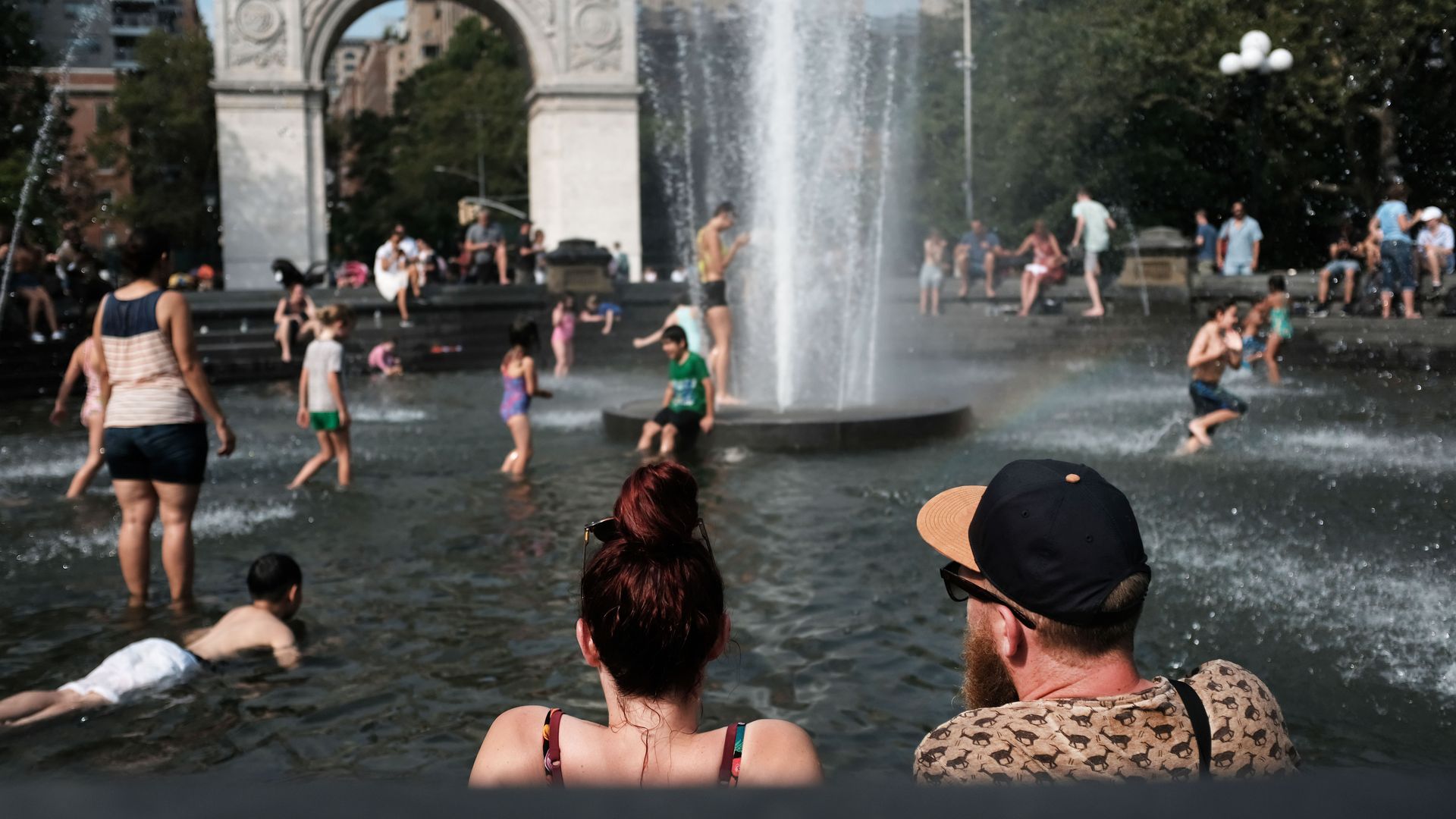
The East Coast of the United States is currently in the grips of a severe and prolonged heat wave, with record-breaking temperatures and stifling humidity affecting millions of people from New England to the Carolinas. This extreme weather event is not only causing widespread discomfort but also posing significant health risks, straining infrastructure, and disrupting daily life.
Unprecedented Temperatures and Humidity
The current heat wave is characterized by unusually high temperatures, with many cities experiencing daytime highs well into the 90s and even surpassing 100 degrees Fahrenheit. What makes this heat wave particularly dangerous is the combination of high temperatures and high humidity, which creates a "feels like" temperature, or heat index, that can be even more oppressive.
The heat index is a measure of how hot it feels when humidity is combined with air temperature. High humidity levels reduce the body’s ability to cool itself through sweating, making it harder to regulate internal body temperature. As a result, even relatively moderate temperatures can feel dangerously hot when humidity is high.
In many parts of the East Coast, the heat index has soared above 100 degrees Fahrenheit, and in some areas, it has even approached or exceeded 110 degrees Fahrenheit. These extreme conditions pose a serious threat to human health, especially for vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and people with chronic medical conditions.
Health Risks and Precautions
The human body can only tolerate a limited amount of heat stress before it begins to malfunction. When the body’s cooling mechanisms are overwhelmed, heat-related illnesses can occur, ranging from mild conditions like heat cramps and heat exhaustion to life-threatening conditions like heat stroke.
Heat cramps are muscle spasms that can occur during or after strenuous activity in hot weather. Heat exhaustion is a more serious condition characterized by symptoms such as heavy sweating, weakness, dizziness, headache, nausea, and vomiting. Heat stroke is the most severe form of heat-related illness and is a medical emergency. Symptoms of heat stroke include a high body temperature (104 degrees Fahrenheit or higher), confusion, disorientation, seizures, and loss of consciousness.
To protect themselves from the health risks of the heat wave, people are advised to take the following precautions:
- Stay in air-conditioned environments as much as possible.
- Drink plenty of fluids, especially water, to stay hydrated.
- Avoid strenuous activity during the hottest part of the day.
- Wear light-colored, loose-fitting clothing.
- Take cool showers or baths to lower body temperature.
- Check on elderly neighbors and relatives to make sure they are safe.
- Never leave children or pets in a parked car, even for a short period of time.
Impact on Infrastructure and Daily Life
The extreme heat is not only affecting human health but also straining infrastructure and disrupting daily life. Power grids are under immense pressure as people crank up their air conditioners to stay cool. This increased demand for electricity can lead to power outages, which can be especially dangerous during a heat wave.
Transportation systems are also being affected by the heat. Roads can buckle and crack under the extreme temperatures, and train tracks can warp, leading to delays and cancellations. Public transportation agencies are taking steps to mitigate these risks, such as reducing train speeds and providing extra water for passengers.
The heat wave is also impacting outdoor activities and events. Many outdoor events have been canceled or postponed, and people are being advised to avoid spending too much time outdoors during the hottest part of the day. Construction workers, farmers, and other outdoor workers are particularly vulnerable to the heat and are taking extra precautions to protect themselves.
Vulnerable Populations
Certain populations are more vulnerable to the effects of heat waves than others. The elderly are particularly at risk because their bodies are less able to regulate temperature effectively. Young children are also vulnerable because they have a higher surface area-to-body mass ratio, which means they can heat up more quickly.
People with chronic medical conditions, such as heart disease, respiratory problems, and diabetes, are also at increased risk of heat-related illnesses. These conditions can make it harder for the body to cope with heat stress.
Low-income communities are also disproportionately affected by heat waves. People in these communities may not have access to air conditioning or other resources to stay cool. They may also live in areas with less green space, which can exacerbate the urban heat island effect.
The Urban Heat Island Effect
The urban heat island effect is a phenomenon in which urban areas are significantly warmer than surrounding rural areas. This is due to a variety of factors, including the abundance of dark surfaces like asphalt and concrete, which absorb more solar radiation than natural surfaces like vegetation. The lack of green space in urban areas also contributes to the heat island effect, as trees and other plants provide shade and cool the air through evapotranspiration.
The urban heat island effect can make heat waves even more dangerous in cities, as temperatures can be several degrees higher than in surrounding areas. This can lead to increased rates of heat-related illnesses and deaths.
Climate Change Connection
While it is difficult to attribute any single weather event directly to climate change, scientists say that heat waves are becoming more frequent, intense, and longer-lasting due to global warming. As the planet warms, average temperatures are rising, and extreme weather events are becoming more common.
Climate models predict that heat waves will continue to become more severe in the future, posing a growing threat to human health and infrastructure. To mitigate the impacts of climate change, it is essential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and transition to a clean energy economy.
Government and Community Response
Governments and communities are taking steps to respond to the heat wave and protect public health. Many cities have opened cooling centers, which are air-conditioned public spaces where people can go to escape the heat. Public health agencies are issuing heat advisories and providing information on how to stay safe during the heat wave.
Community organizations are also playing a role in helping vulnerable populations. These organizations are providing transportation to cooling centers, delivering water and other supplies to those in need, and checking on elderly and disabled residents.
Long-Term Solutions
While immediate responses are crucial during a heat wave, long-term solutions are needed to address the growing threat of extreme heat. These solutions include:
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions to slow down climate change.
- Investing in infrastructure improvements to make power grids and transportation systems more resilient to extreme weather.
- Planting more trees and creating more green space in urban areas to reduce the urban heat island effect.
- Improving building codes to require more energy-efficient construction and better insulation.
- Developing early warning systems to alert people to impending heat waves.
- Educating the public about the risks of heat waves and how to stay safe.
Conclusion
The current heat wave on the East Coast is a stark reminder of the growing threat of extreme heat. As climate change continues to worsen, heat waves are likely to become more frequent, intense, and longer-lasting. It is essential to take steps to protect public health, improve infrastructure, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate the impacts of extreme heat. By working together, we can build more resilient communities and protect ourselves from the growing threat of climate change. The ongoing heat wave serves as a critical call to action, underscoring the urgency of addressing climate change and preparing for a future where extreme weather events are increasingly common. Individual actions, community initiatives, and government policies must align to safeguard the health and well-being of all citizens in the face of a changing climate.
