“Homeschooling Rates: Trends, Factors, and Implications
Related Articles Homeschooling Rates: Trends, Factors, and Implications
- Medicare Drug Price Cap: A Comprehensive Analysis
- Effective Cyber Defense Strategies for Enhanced Cybersecurity
- Mastering Security Incident Handling: A Comprehensive Guide to Protect Your Cybersecurity
- Early Warning System: Proactive Security Breach Detection for Enhanced Cybersecurity
- The Permian Powerhouse: Texas Oil Production And Its Global Impact
Introduction
With great enthusiasm, let’s explore interesting topics related to Homeschooling Rates: Trends, Factors, and Implications. Let’s knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Homeschooling Rates: Trends, Factors, and Implications
Homeschooling, an educational approach where parents or guardians educate their children at home rather than sending them to traditional public or private schools, has witnessed a significant surge in popularity over the past few decades. This trend has sparked considerable interest among educators, policymakers, and researchers, prompting them to investigate the underlying factors driving homeschooling growth and its potential implications for students, families, and society as a whole.
Historical Overview of Homeschooling
Homeschooling is not a new phenomenon. In fact, it was the predominant form of education throughout history, with parents or tutors assuming responsibility for imparting knowledge and skills to children. Formal schooling emerged relatively recently, gaining traction during the Industrial Revolution as societies sought to standardize education and prepare individuals for the workforce.
However, homeschooling never entirely disappeared. It persisted as a niche option for families seeking personalized education, religious instruction, or specialized learning environments. In the United States, homeschooling experienced a resurgence in the 1970s and 1980s, fueled by concerns about the quality of public schools, the desire for greater parental control over education, and the rise of conservative religious movements.
Recent Trends in Homeschooling Rates
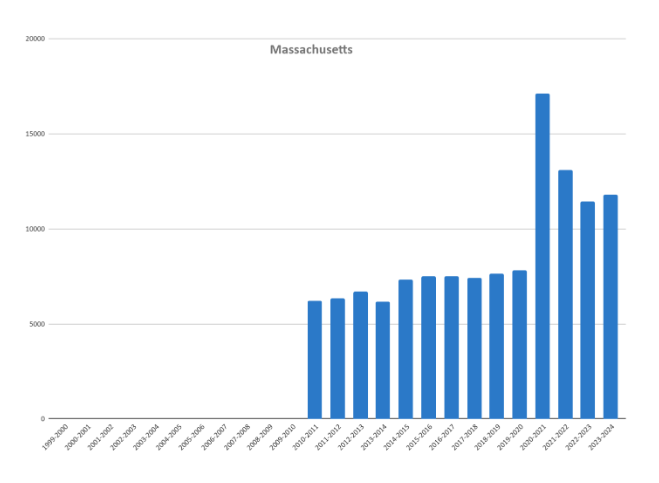
Homeschooling rates have steadily increased in recent years, particularly in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. According to data from the U.S. Census Bureau, the percentage of homeschooling households more than doubled from 5.4% in spring 2020 to 11.1% in fall 2020. While homeschooling rates have since declined somewhat, they remain significantly higher than pre-pandemic levels.
The National Home Education Research Institute (NHERI) estimates that there are currently around 3.7 million homeschool students in the United States, representing approximately 6% of the school-age population. Homeschooling rates vary considerably across states, with some states having significantly higher percentages of homeschool students than others.
Factors Influencing Homeschooling Rates
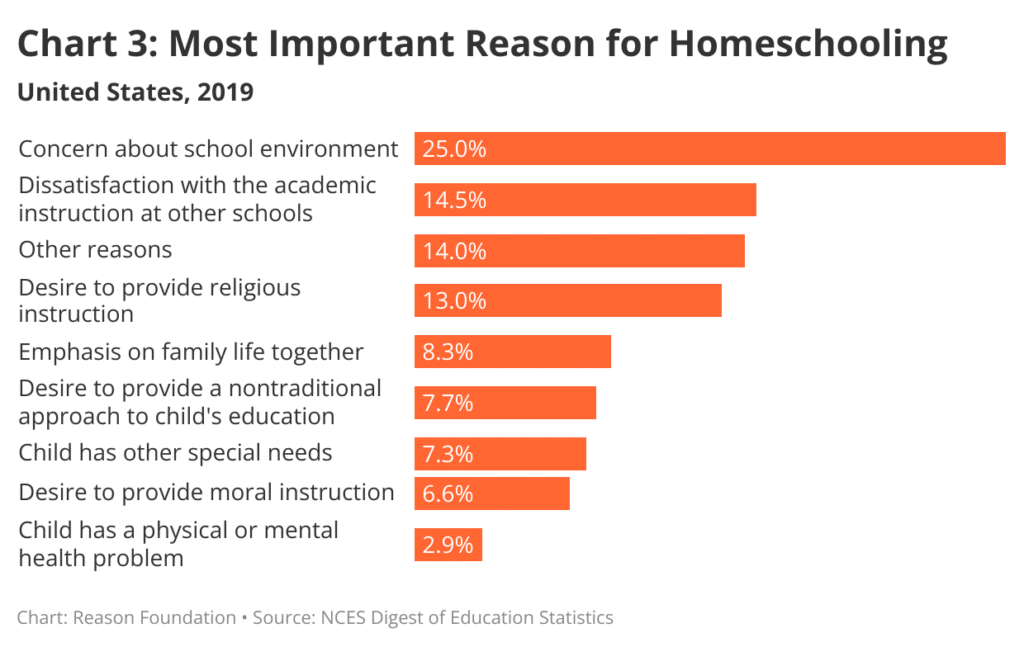
Several factors contribute to the growth of homeschooling rates. These include:
-
Dissatisfaction with Traditional Schools: Many parents choose to homeschool because they are dissatisfied with the quality of education provided by traditional schools. Concerns about large class sizes, standardized testing, disciplinary issues, and lack of individualized attention can lead parents to seek alternative educational options.
-
Desire for Personalized Education: Homeschooling allows parents to tailor the curriculum and teaching methods to meet the unique needs and interests of their children. This personalized approach can be particularly beneficial for students with learning disabilities, gifted students, or those who thrive in a more flexible learning environment.
-
Religious or Moral Beliefs: For some families, homeschooling is driven by religious or moral beliefs. Parents may want to instill specific values or teachings that are not emphasized in traditional schools. They may also be concerned about the influence of secular culture on their children.
-
Safety Concerns: Safety concerns, such as bullying, violence, and drug use, can also prompt parents to homeschool their children. Parents may believe that homeschooling provides a safer and more nurturing environment for their children to learn and grow.
-
Flexibility and Convenience: Homeschooling offers greater flexibility and convenience compared to traditional schooling. Parents can set their own schedules, choose their own curriculum, and travel or pursue other activities without being constrained by school calendars.
-
COVID-19 Pandemic: The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on homeschooling rates. School closures and concerns about the safety of in-person learning led many parents to temporarily or permanently switch to homeschooling.
Demographic Characteristics of Homeschooling Families
Homeschooling families come from diverse backgrounds and represent a wide range of socioeconomic levels, educational backgrounds, and family structures. However, some demographic patterns have been observed in homeschooling families:
- Income: Homeschooling families tend to have higher household incomes than families who send their children to traditional schools. This may be due to the fact that homeschooling often requires one parent to stay home or work part-time, which can be a financial burden for some families.
- Education: Parents who homeschool tend to have higher levels of education than parents who send their children to traditional schools. This may be because homeschooling requires parents to take on the role of teacher, which can be challenging for parents with limited educational backgrounds.
- Family Structure: Homeschooling families are more likely to have two parents in the household than families who send their children to traditional schools. This may be because homeschooling requires a significant time commitment from parents, which can be difficult for single-parent families.
- Race and Ethnicity: Homeschooling rates vary across racial and ethnic groups. Historically, homeschooling was more prevalent among white families, but homeschooling rates have been increasing among Black and Hispanic families in recent years.
Academic Outcomes of Homeschool Students
One of the most frequently asked questions about homeschooling is whether homeschool students perform as well academically as students in traditional schools. Research on this topic has generally found that homeschool students perform as well or better than their peers in traditional schools on standardized tests.
A meta-analysis of studies on homeschooling found that homeschool students scored significantly higher than public school students on standardized tests across all subjects. Homeschool students also tend to have higher grade point averages and are more likely to attend college.
However, it is important to note that the academic outcomes of homeschool students can vary depending on a number of factors, including the parents’ educational background, the quality of the curriculum used, and the level of support provided to the student.
Socialization of Homeschool Students
Another common concern about homeschooling is whether homeschool students are adequately socialized. Some critics argue that homeschool students may lack the social interaction and opportunities for peer learning that are available in traditional schools.
However, research on the socialization of homeschool students has generally found that they are well-adjusted and have strong social skills. Homeschool students often participate in a variety of extracurricular activities, such as sports, clubs, and volunteer organizations, which provide opportunities for social interaction.
Additionally, some studies have found that homeschool students may have better social skills than students in traditional schools. This may be because homeschool students have more opportunities to interact with adults and children of different ages, which can help them develop strong communication and social skills.
Legal and Regulatory Framework for Homeschooling
The legal and regulatory framework for homeschooling varies considerably across states. Some states have very few regulations on homeschooling, while others have more stringent requirements.
In general, states require homeschool parents to notify the state or local school district of their intent to homeschool, provide instruction in certain subjects, and assess their children’s progress. Some states also require homeschool parents to have a certain level of education or to pass a background check.
The legal and regulatory framework for homeschooling is constantly evolving, and parents who are considering homeschooling should familiarize themselves with the laws and regulations in their state.
Challenges and Considerations for Homeschooling Families
While homeschooling can be a rewarding experience for both parents and children, it also presents a number of challenges and considerations. These include:
- Time Commitment: Homeschooling requires a significant time commitment from parents. Parents must be willing to dedicate time to planning lessons, teaching, and grading assignments.
- Financial Costs: Homeschooling can be expensive. Parents must purchase curriculum materials, supplies, and other resources. They may also need to forgo income if one parent stays home to homeschool.
- Social Isolation: Homeschooling can lead to social isolation for both parents and children. Parents may miss the social interaction and support that they would get from other parents at a traditional school. Children may miss the social interaction and peer learning that they would get from being in a classroom with other students.
- Burnout: Homeschooling can be stressful and lead to burnout for parents. Parents may feel overwhelmed by the responsibility of educating their children and may struggle to balance homeschooling with other responsibilities.
- Curriculum Development: Developing a curriculum is challenging. Parents may find it difficult to choose appropriate materials and ensure that their children are learning what they need to know.
- Lack of Resources: Homeschooling families may lack access to the resources that are available to students in traditional schools, such as libraries, science labs, and art studios.
Implications of Homeschooling for Society
The growth of homeschooling has a number of implications for society. These include:
- Impact on Public Schools: The growth of homeschooling can have a negative impact on public schools. As more students leave public schools to homeschool, public schools may lose funding and resources.
- Equity Concerns: Homeschooling may exacerbate existing inequalities in education. Families with higher incomes and more education are more likely to homeschool, which could lead to a widening gap between the academic outcomes of students from different socioeconomic backgrounds.
- Workforce Development: Homeschooling may have implications for workforce development. Some critics argue that homeschool students may lack the skills and knowledge that are needed to succeed in the workforce.
- Civic Engagement: Homeschooling may have implications for civic engagement. Some critics argue that homeschool students may be less likely to participate in civic activities, such as voting and volunteering.
Conclusion
Homeschooling rates have been on the rise in recent years, driven by a variety of factors, including dissatisfaction with traditional schools, the desire for personalized education, religious or moral beliefs, and safety concerns. Homeschooling offers a number of potential benefits for students and families, but it also presents a number of challenges and considerations. The growth of homeschooling has a number of implications for society, including the impact on public schools, equity concerns, workforce development, and civic engagement. As homeschooling continues to grow in popularity, it is important for educators, policymakers, and researchers to continue to study its impact and to develop policies that support both homeschool families and traditional schools.