“Medicaid Coverage Expansion: A Critical Tool for Improving Health Outcomes and Reducing Disparities
Related Articles Medicaid Coverage Expansion: A Critical Tool for Improving Health Outcomes and Reducing Disparities
- Master Cybersecurity with Cutting-Edge Threat Monitoring
- The Resurgence Of US Labor Union Strikes: Causes, Impact, And Future Prospects
- The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Security Event Management
- Cutting-Edge Endpoint Threat Prevention: Securing Endpoints
- Ukraine Military Aid Package: A Lifeline In The Face Of Aggression
Introduction
We will be happy to explore interesting topics related to Medicaid Coverage Expansion: A Critical Tool for Improving Health Outcomes and Reducing Disparities. Let’s knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Medicaid Coverage Expansion: A Critical Tool for Improving Health Outcomes and Reducing Disparities
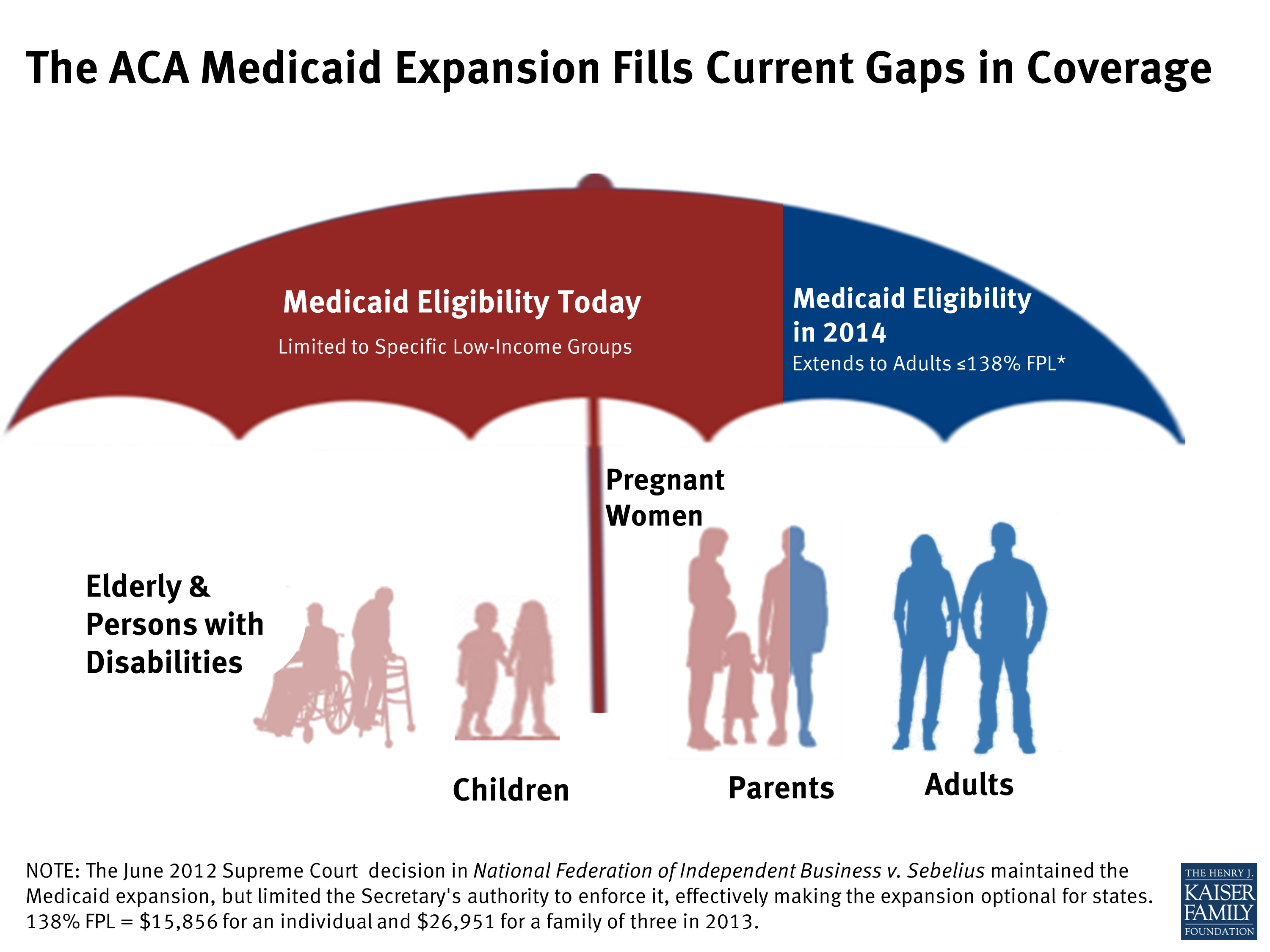
Medicaid is a joint federal and state program that provides health coverage to millions of low-income Americans. It is the largest source of health coverage in the United States, covering more than 75 million people, including children, pregnant women, seniors, and people with disabilities. Medicaid plays a critical role in ensuring that low-income individuals and families have access to essential healthcare services.
In 2010, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) was signed into law. The ACA included a provision that expanded Medicaid eligibility to nearly all adults with incomes up to 138% of the federal poverty level. The ACA’s Medicaid expansion aimed to reduce the number of uninsured Americans, improve access to care, and reduce health disparities.
As of November 2023, 40 states and the District of Columbia have adopted Medicaid expansion. The expansion has had a significant impact on the health and well-being of millions of Americans. In this article, we will discuss the benefits of Medicaid expansion, the challenges of implementation, and the future of Medicaid expansion in the United States.
Benefits of Medicaid Expansion
Medicaid expansion has had a number of positive effects, including:
- Increased access to care: Medicaid expansion has significantly increased access to healthcare for low-income individuals. Studies have shown that Medicaid expansion has led to a decrease in the number of uninsured Americans and an increase in the number of people who have a usual source of care. For example, a study by the Kaiser Family Foundation found that Medicaid expansion led to a 7.3 percentage point decrease in the uninsured rate among low-income adults.
- Improved health outcomes: Medicaid expansion has been linked to improved health outcomes, such as lower mortality rates, fewer hospitalizations, and better management of chronic conditions. A study by the National Bureau of Economic Research found that Medicaid expansion led to a 6.1% reduction in mortality rates among adults aged 20-64.
- Reduced financial strain: Medicaid expansion has helped to reduce the financial strain on low-income families by providing them with access to affordable healthcare. Medicaid expansion has also been shown to reduce medical debt and improve credit scores. A study by the Urban Institute found that Medicaid expansion led to a $1,000 reduction in medical debt among low-income adults.
- Economic benefits: Medicaid expansion has also had a positive impact on state economies. Medicaid expansion has created jobs, increased economic activity, and generated tax revenue. A study by the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities found that Medicaid expansion created 537,000 jobs and generated $38.8 billion in economic activity in 2016.
- Reduced disparities: Medicaid expansion has helped to reduce health disparities by providing coverage to populations that are disproportionately uninsured, such as people of color and low-income individuals. A study by the Commonwealth Fund found that Medicaid expansion led to a significant reduction in racial and ethnic disparities in health coverage.
Challenges of Implementation
Despite the many benefits of Medicaid expansion, there have also been some challenges to implementation. These challenges include:
- Political opposition: Medicaid expansion has faced political opposition in some states, particularly from Republican lawmakers who are concerned about the cost of the program. In some states, political opposition has led to delays in implementation or to the adoption of alternative expansion models that provide less comprehensive coverage.
- Administrative complexity: Medicaid expansion can be administratively complex, requiring states to update their eligibility systems and train staff to enroll new beneficiaries. Some states have struggled to implement Medicaid expansion smoothly, leading to delays in coverage and confusion among beneficiaries.
- Provider capacity: In some areas, there may not be enough healthcare providers to meet the increased demand for services that results from Medicaid expansion. This can lead to longer wait times for appointments and difficulty accessing care.
- Sustainability: Some states have raised concerns about the long-term sustainability of Medicaid expansion, particularly as the federal government’s share of the cost of expansion decreases over time. States are responsible for paying a portion of the cost of Medicaid expansion, and some states may struggle to afford this cost in the future.
The Future of Medicaid Expansion
The future of Medicaid expansion in the United States is uncertain. While the ACA remains the law of the land, there have been ongoing efforts to repeal or weaken the law. If the ACA were repealed, Medicaid expansion would likely be eliminated, leaving millions of Americans without health coverage.
Even if the ACA remains in place, there is no guarantee that all states will eventually adopt Medicaid expansion. Some states may continue to resist expansion due to political opposition or concerns about cost. However, there is also reason to be optimistic about the future of Medicaid expansion. As more states see the benefits of expansion, they may be more likely to adopt it. Additionally, the federal government could provide incentives to encourage states to expand Medicaid.
Conclusion
Medicaid expansion is a critical tool for improving health outcomes, reducing health disparities, and strengthening state economies. While there have been some challenges to implementation, the benefits of expansion far outweigh the costs. As more states adopt Medicaid expansion, the number of uninsured Americans will continue to decline, and more people will have access to the healthcare they need to live healthy and productive lives.
Medicaid expansion is an investment in the health and well-being of our nation. It is a policy that has been proven to work, and it should be supported by policymakers at the federal and state levels. By expanding Medicaid, we can create a healthier and more equitable society for all.
Additional Considerations:
- The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic: The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of Medicaid as a safety net for low-income Americans. During the pandemic, millions of people lost their jobs and their health insurance. Medicaid expansion has helped to ensure that these individuals have access to healthcare during this difficult time.
- The Role of Medicaid in Addressing the Opioid Crisis: Medicaid plays a critical role in addressing the opioid crisis. Medicaid covers substance use disorder treatment services, and Medicaid expansion has helped to increase access to these services. Studies have shown that Medicaid expansion has been linked to a reduction in opioid overdose deaths.
- The Potential for Innovation in Medicaid: Medicaid is a complex program, but it also has the potential for innovation. States are experimenting with new ways to deliver healthcare to Medicaid beneficiaries, such as value-based care models and telehealth. These innovations could help to improve the quality of care and reduce costs.
- The Importance of Outreach and Enrollment: Even in states that have expanded Medicaid, it is important to conduct outreach and enrollment efforts to ensure that eligible individuals are aware of the program and have access to coverage. Many people who are eligible for Medicaid do not know it, or they may be intimidated by the enrollment process.
- The Need for Continued Monitoring and Evaluation: It is important to continue to monitor and evaluate the impact of Medicaid expansion to ensure that it is achieving its goals. This includes tracking health outcomes, access to care, and costs. By monitoring and evaluating Medicaid expansion, we can identify areas where the program can be improved.
Conclusion (Expanded)
Medicaid expansion stands as a landmark achievement in the ongoing effort to improve healthcare access and outcomes for vulnerable populations in the United States. The evidence overwhelmingly demonstrates that expanding Medicaid coverage has yielded significant benefits, including increased access to care, improved health outcomes, reduced financial strain on low-income families, positive economic impacts, and a reduction in health disparities.
While challenges related to political opposition, administrative complexity, provider capacity, and long-term sustainability exist, they should not overshadow the transformative potential of Medicaid expansion. States that have embraced expansion have witnessed firsthand the positive impact on their residents’ health and well-being, as well as on their economies.
As we look to the future, it is imperative that policymakers at both the federal and state levels prioritize the expansion and strengthening of Medicaid. This includes addressing the challenges that hinder implementation, fostering innovation in program design and delivery, and ensuring that outreach and enrollment efforts effectively reach eligible individuals.
The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the critical role of Medicaid as a safety net during times of economic hardship and public health crises. Medicaid’s ability to provide access to care for those who have lost their jobs and health insurance has been invaluable. Furthermore, Medicaid plays a crucial role in addressing the opioid crisis by providing coverage for substance use disorder treatment services.
By continuing to invest in Medicaid expansion and innovation, we can create a healthcare system that is more equitable, accessible, and effective for all Americans. Medicaid expansion is not just a healthcare policy; it is an investment in the health, well-being, and economic prosperity of our nation. It is a policy that deserves continued support and expansion to ensure that all individuals have the opportunity to live healthy and productive lives. The continued monitoring and evaluation of Medicaid expansion are crucial to ensuring its effectiveness and identifying areas for improvement. Through data-driven decision-making and a commitment to innovation, we can maximize the benefits of Medicaid expansion and create a healthier and more equitable society for all.