“Public Health Policy Changes: Navigating Complex Landscapes and Improving Population Health
Related Articles Public Health Policy Changes: Navigating Complex Landscapes and Improving Population Health
- Leading-Edge Endpoint Security: Comprehensive Protection Against Cyber Threats
- XRP Price Volatility: Understanding The Factors And Navigating The Risks
- Supreme Court Overturns Roe V. Wade, Ending Constitutional Right To Abortion
- The End Of Affirmative Action: The Ivy League, Diversity, And The Future Of College Admissions
- Michael Saylor’s Bitcoin Strategy: A Deep Dive Into MicroStrategy’s Bold Bet
Introduction
On this special occasion, we are happy to review interesting topics related to Public Health Policy Changes: Navigating Complex Landscapes and Improving Population Health. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Public Health Policy Changes: Navigating Complex Landscapes and Improving Population Health

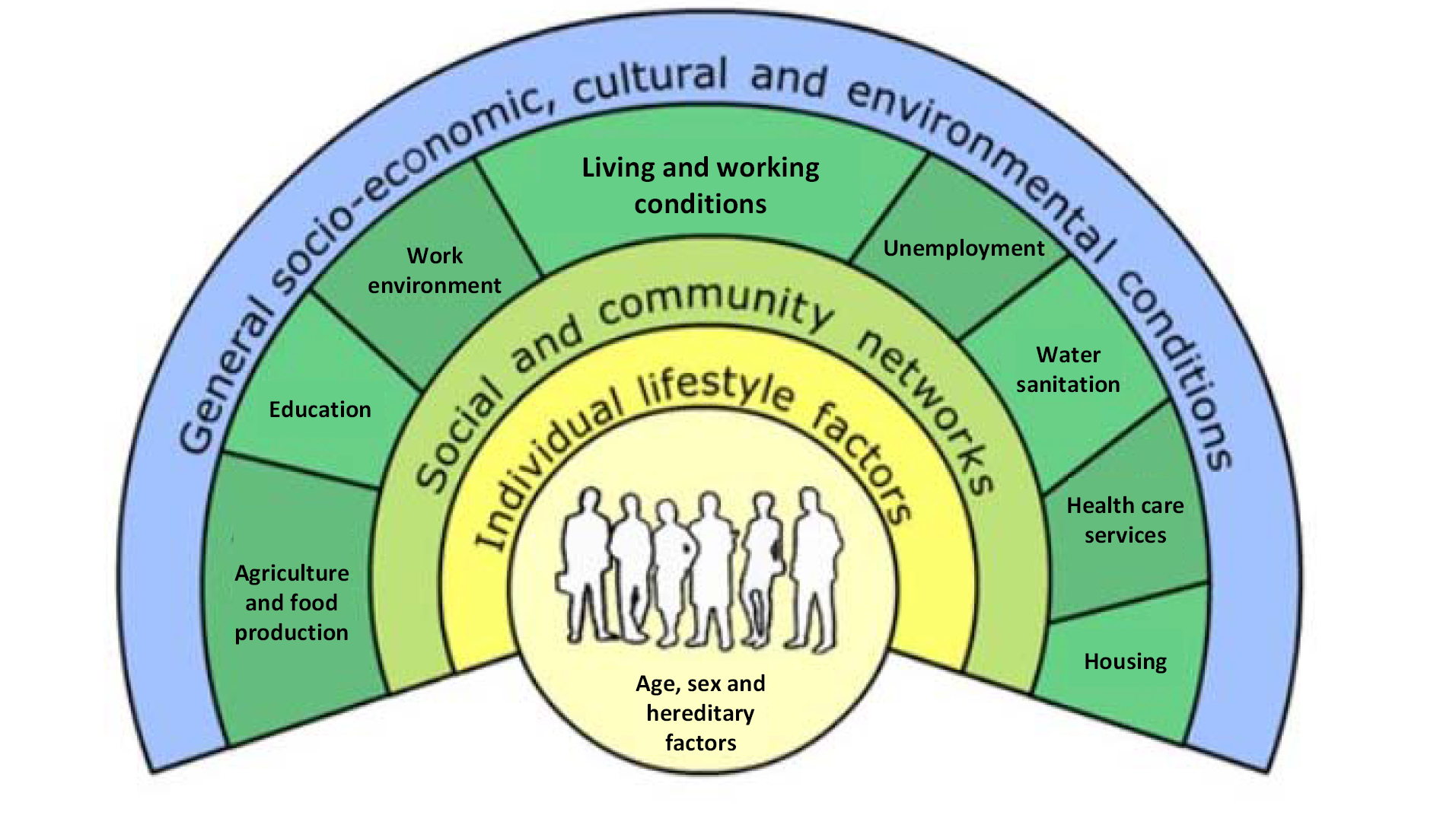
Public health policies are crucial instruments that governments and organizations use to improve the health and well-being of populations. These policies encompass a wide range of interventions, including laws, regulations, programs, and initiatives, all aimed at preventing disease, promoting healthy behaviors, and ensuring access to healthcare services. In a constantly evolving world, public health policies must adapt to address emerging health challenges, scientific advancements, and societal shifts. This article explores the dynamics of public health policy changes, examining the factors that drive these changes, the processes involved, and the potential impact on population health.
Drivers of Public Health Policy Change
Several factors contribute to the need for changes in public health policies. These drivers can be broadly categorized as follows:
-
Emerging Health Challenges: The emergence of new infectious diseases, such as COVID-19, or the rise in chronic diseases, such as diabetes and heart disease, necessitates policy changes to address these challenges effectively. Public health policies must be adapted to prevent and control the spread of infectious diseases, promote healthy lifestyles to prevent chronic diseases, and ensure access to appropriate healthcare services.
-
Scientific Advancements: Scientific discoveries and technological advancements can provide new insights into disease prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. Public health policies must be updated to incorporate these advancements and ensure that the public benefits from them. For example, the development of new vaccines or therapies may require policy changes to ensure their availability and accessibility to those who need them.
-
Societal Shifts: Changes in societal norms, values, and demographics can also drive public health policy changes. For example, the aging of the population may require policy changes to address the healthcare needs of older adults. Similarly, increasing awareness of health disparities may necessitate policy changes to promote health equity.
-
Economic Factors: Economic conditions can significantly impact public health. Economic recessions can lead to increased poverty, unemployment, and food insecurity, which can negatively affect health outcomes. Public health policies must be adapted to mitigate the negative health impacts of economic downturns and ensure that vulnerable populations have access to essential resources.
-
Political Considerations: Political ideologies and priorities can also influence public health policy changes. Different political parties may have different views on the role of government in public health and the types of policies that should be implemented. Changes in political leadership can lead to shifts in public health policy priorities.
Processes Involved in Public Health Policy Change
Public health policy change is a complex process that typically involves several stages:
-
Problem Identification: The first step in the policy change process is to identify a public health problem that needs to be addressed. This can involve collecting data on disease prevalence, risk factors, and health outcomes. It can also involve engaging with stakeholders, such as healthcare providers, community organizations, and the public, to understand their perspectives on the problem.
-
Policy Formulation: Once a problem has been identified, the next step is to develop potential policy solutions. This can involve conducting research on effective interventions, consulting with experts, and engaging with stakeholders to gather input on different policy options.
-
Policy Adoption: After policy options have been developed, the next step is to adopt a specific policy. This typically involves legislative action or regulatory rulemaking. Policymakers must consider the potential impact of the policy on different groups, the costs and benefits of the policy, and the political feasibility of the policy.
-
Policy Implementation: Once a policy has been adopted, the next step is to implement it. This can involve developing guidelines, training healthcare providers, and conducting public awareness campaigns. Effective implementation requires careful planning, coordination, and monitoring.
-
Policy Evaluation: After a policy has been implemented, it is important to evaluate its effectiveness. This can involve collecting data on health outcomes, assessing the impact of the policy on different groups, and identifying any unintended consequences. Policy evaluations can help policymakers determine whether a policy is achieving its intended goals and whether any changes are needed.
Impact of Public Health Policy Changes
Public health policy changes can have a significant impact on population health. Effective policies can prevent disease, promote healthy behaviors, and improve access to healthcare services. However, policy changes can also have unintended consequences, and it is important to carefully consider the potential impact of any policy before it is implemented.
-
Improved Health Outcomes: Public health policies can lead to improved health outcomes by preventing disease, promoting healthy behaviors, and ensuring access to healthcare services. For example, policies that promote vaccination can reduce the incidence of infectious diseases. Policies that encourage healthy eating and physical activity can reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Policies that expand access to healthcare can improve health outcomes for vulnerable populations.
-
Reduced Healthcare Costs: Public health policies can also lead to reduced healthcare costs by preventing disease and promoting early detection and treatment. For example, policies that promote smoking cessation can reduce the incidence of lung cancer and other smoking-related diseases, which can lead to significant cost savings. Policies that encourage early detection of cancer can improve treatment outcomes and reduce the need for expensive treatments.
-
Health Equity: Public health policies can play a crucial role in promoting health equity by addressing health disparities and ensuring that all individuals have the opportunity to achieve optimal health. Policies that target specific populations, such as low-income communities or racial and ethnic minorities, can help to reduce health disparities. Policies that address social determinants of health, such as poverty, education, and housing, can also promote health equity.
-
Unintended Consequences: Public health policy changes can also have unintended consequences. For example, policies that restrict access to certain products or services may lead to unintended consequences, such as the development of black markets or the increased use of alternative products or services that may be even more harmful. It is important to carefully consider the potential unintended consequences of any policy before it is implemented.
Examples of Public Health Policy Changes
Numerous examples of public health policy changes have had a significant impact on population health. Here are a few notable examples:
-
Tobacco Control Policies: Tobacco control policies, such as cigarette taxes, smoke-free laws, and advertising restrictions, have been effective in reducing smoking rates and improving public health. These policies have led to a decline in smoking-related diseases, such as lung cancer and heart disease.
-
Vaccination Policies: Vaccination policies, such as mandatory vaccination for school children, have been effective in preventing the spread of infectious diseases. These policies have led to a significant reduction in the incidence of diseases such as measles, mumps, and rubella.
-
Food Safety Policies: Food safety policies, such as regulations on food handling and processing, have been effective in preventing foodborne illnesses. These policies have led to a reduction in the incidence of foodborne diseases such as salmonellosis and E. coli infections.
-
Motor Vehicle Safety Policies: Motor vehicle safety policies, such as seat belt laws and drunk driving laws, have been effective in reducing traffic fatalities. These policies have led to a significant reduction in the number of deaths and injuries caused by motor vehicle crashes.
-
Affordable Care Act (ACA): The Affordable Care Act (ACA) is a landmark public health policy that has expanded access to health insurance for millions of Americans. The ACA has led to a reduction in the uninsured rate and improved access to healthcare services for vulnerable populations.
Challenges in Public Health Policy Change
Despite the potential benefits of public health policy changes, there are also several challenges involved in implementing these changes. These challenges include:
-
Political Opposition: Public health policy changes can face political opposition from various groups, such as industry lobbyists, special interest groups, and political parties with different ideologies. Overcoming political opposition requires strong advocacy, public support, and evidence-based arguments.
-
Lack of Funding: Public health policy changes often require significant funding for implementation and evaluation. Securing adequate funding can be a challenge, especially in times of economic constraints.
-
Implementation Challenges: Implementing public health policies can be complex and require careful planning, coordination, and monitoring. Challenges can arise from lack of resources, inadequate infrastructure, or resistance from stakeholders.
-
Unintended Consequences: Public health policy changes can have unintended consequences that can be difficult to predict. It is important to carefully consider the potential unintended consequences of any policy before it is implemented.
-
Evaluation Challenges: Evaluating the effectiveness of public health policies can be challenging. It can be difficult to isolate the impact of a policy from other factors that may be influencing health outcomes.
Conclusion
Public health policy changes are essential for addressing emerging health challenges, incorporating scientific advancements, and adapting to societal shifts. The process of public health policy change is complex and involves several stages, including problem identification, policy formulation, policy adoption, policy implementation, and policy evaluation. Public health policy changes can have a significant impact on population health, leading to improved health outcomes, reduced healthcare costs, and health equity. However, there are also several challenges involved in implementing public health policy changes, including political opposition, lack of funding, implementation challenges, unintended consequences, and evaluation challenges. By understanding the drivers, processes, and challenges involved in public health policy change, policymakers can develop and implement effective policies that improve the health and well-being of populations.