“Ransomware Attack Targets U.S. Hospitals: A Growing Threat to Healthcare
Related Articles Ransomware Attack Targets U.S. Hospitals: A Growing Threat to Healthcare
- NOAA Warns Of Worsening Conditions: A Deep Dive Into The Looming Environmental Crisis
- Military Deployments: A Comprehensive Overview
- Memorial Day Airport Delays: Causes, Impact, And How To Navigate Them
- Auto Dealers Report Supply Chain Relief: Is The End Of The Shortage In Sight?
- Network Security: The Ultimate Guide to Protecting Your Business
Introduction
With great enthusiasm, let’s explore interesting topics related to Ransomware Attack Targets U.S. Hospitals: A Growing Threat to Healthcare. Let’s knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Ransomware Attack Targets U.S. Hospitals: A Growing Threat to Healthcare

In recent years, ransomware attacks have become an increasingly prevalent and sophisticated threat to organizations across various sectors. Among the most vulnerable targets are healthcare providers, particularly U.S. hospitals, which are often ill-equipped to defend against these malicious cyberattacks. The consequences of ransomware attacks on hospitals can be devastating, leading to disruptions in patient care, financial losses, and reputational damage.
Understanding Ransomware Attacks
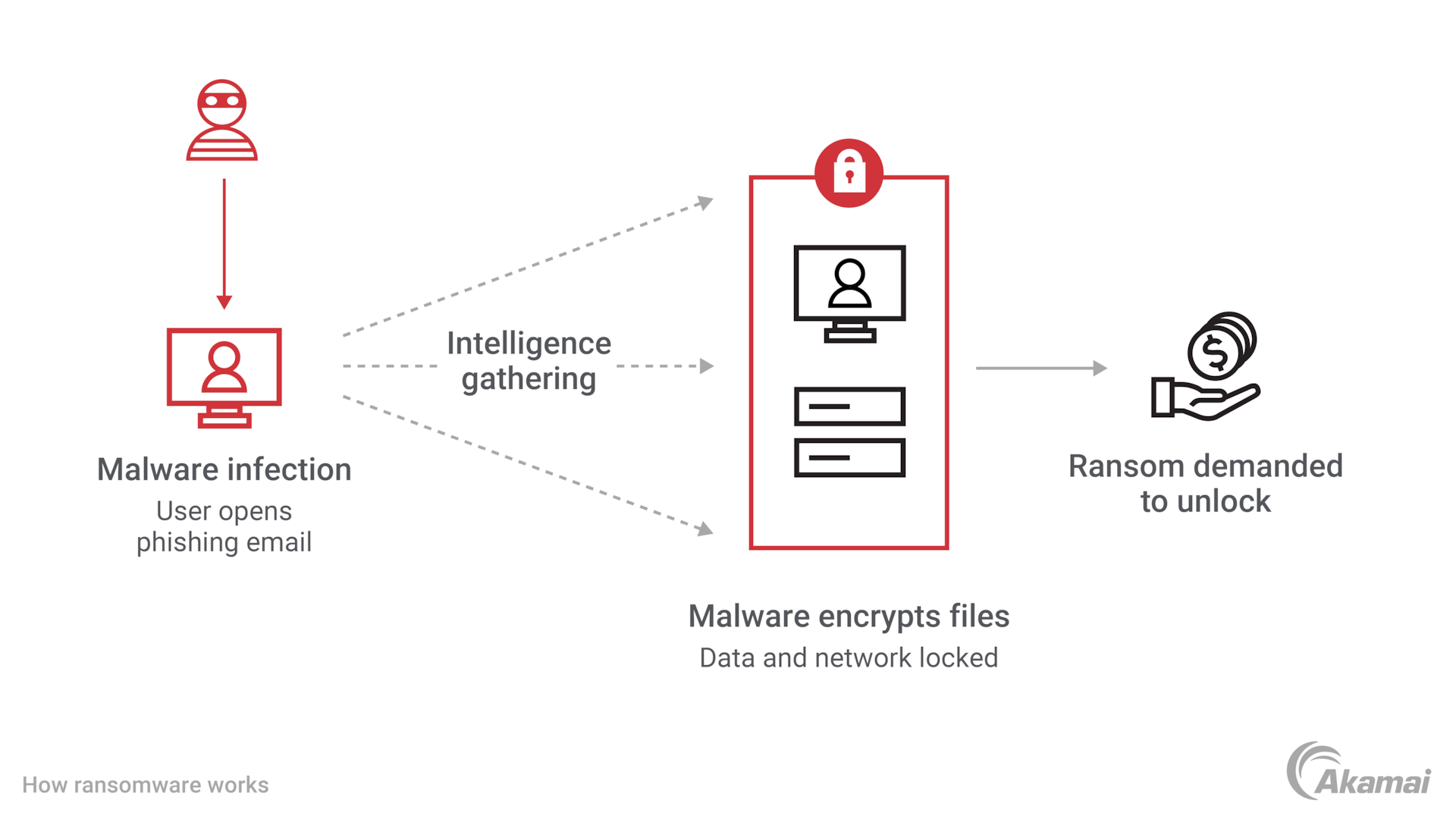
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts a victim’s files, rendering them inaccessible. Attackers then demand a ransom payment, typically in cryptocurrency, in exchange for the decryption key. Ransomware attacks can be carried out through various means, including phishing emails, malicious software downloads, and exploiting vulnerabilities in computer systems.
Once ransomware infects a system, it spreads rapidly throughout the network, encrypting files on servers, workstations, and other connected devices. The attackers then leave a ransom note, which typically includes instructions on how to pay the ransom and recover the encrypted files.
Why Hospitals Are Vulnerable Targets
Hospitals are particularly vulnerable to ransomware attacks for several reasons:
- Reliance on outdated systems: Many hospitals rely on outdated computer systems and software, which often have known vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers.
- Limited cybersecurity resources: Hospitals often have limited cybersecurity resources, including staff, budget, and technology, making it difficult to implement and maintain robust security measures.
- High-value data: Hospitals store vast amounts of sensitive patient data, including medical records, insurance information, and financial details. This data is highly valuable to attackers, who can sell it on the dark web or use it for identity theft.
- Critical infrastructure: Hospitals provide essential healthcare services, and any disruption to their operations can have serious consequences for patients. This makes hospitals more likely to pay the ransom in order to restore their systems quickly.
- Interconnected devices: Modern hospitals rely on a wide range of interconnected devices, including medical equipment, monitoring systems, and diagnostic tools. These devices can be vulnerable to ransomware attacks, and if compromised, they can disrupt patient care and potentially endanger lives.
Impact of Ransomware Attacks on Hospitals
Ransomware attacks can have a significant impact on hospitals, including:
- Disruption of patient care: Ransomware attacks can disrupt patient care by preventing access to medical records, delaying or canceling procedures, and diverting patients to other facilities.
- Financial losses: Ransomware attacks can result in significant financial losses for hospitals, including the cost of ransom payments, system restoration, and lost revenue.
- Reputational damage: Ransomware attacks can damage a hospital’s reputation, leading to a loss of patient trust and difficulty attracting new patients.
- Legal and regulatory consequences: Hospitals that fail to protect patient data from ransomware attacks may face legal and regulatory consequences, including fines and lawsuits.
- Risk to patient safety: In extreme cases, ransomware attacks can pose a direct risk to patient safety. For example, if a hospital’s monitoring systems are compromised, it may not be able to detect and respond to critical changes in a patient’s condition.
Recent Ransomware Attacks on U.S. Hospitals
In recent years, there have been numerous ransomware attacks on U.S. hospitals, including:
- Universal Health Services (UHS) Attack (2020): In September 2020, UHS, one of the largest hospital chains in the U.S., was hit by a ransomware attack that disrupted operations at hundreds of its facilities. The attack forced hospitals to divert patients, cancel surgeries, and rely on paper records.
- Ransomware Attack on Vermont Hospital (2023): A ransomware attack on a Vermont hospital in February 2023 disrupted access to electronic systems for weeks, causing delays in patient care and financial losses.
- CommonSpirit Health Attack (2022): In October 2022, CommonSpirit Health, one of the largest nonprofit health systems in the U.S., experienced a ransomware attack that affected multiple hospitals and clinics across the country. The attack disrupted patient care, delayed procedures, and compromised patient data.
- Hollywood Presbyterian Medical Center Attack (2016): In 2016, Hollywood Presbyterian Medical Center in Los Angeles paid a ransom of $17,000 in Bitcoin to regain access to its computer systems after a ransomware attack. The attack disrupted patient care for several days and highlighted the vulnerability of hospitals to ransomware.
Preventing Ransomware Attacks on Hospitals
There are several steps that hospitals can take to prevent ransomware attacks:
- Implement a strong cybersecurity program: Hospitals should implement a comprehensive cybersecurity program that includes regular risk assessments, security awareness training for employees, and robust security measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and antivirus software.
- Keep systems up to date: Hospitals should keep their computer systems and software up to date with the latest security patches. This will help to protect against known vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers.
- Use strong passwords: Hospitals should require employees to use strong passwords and to change them regularly.
- Implement multi-factor authentication: Hospitals should implement multi-factor authentication for all critical systems. This will add an extra layer of security and make it more difficult for attackers to gain access to systems even if they have stolen passwords.
- Back up data regularly: Hospitals should back up their data regularly and store the backups in a secure location. This will allow them to restore their systems quickly in the event of a ransomware attack.
- Develop an incident response plan: Hospitals should develop an incident response plan that outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a ransomware attack. This plan should include procedures for identifying and containing the attack, restoring systems, and communicating with patients and the public.
- Segment the network: Hospitals should segment their networks to limit the spread of ransomware. This can be done by creating separate networks for different departments or functions.
- Monitor network traffic: Hospitals should monitor their network traffic for suspicious activity. This can help to detect ransomware attacks early on, before they can cause significant damage.
- Partner with cybersecurity experts: Hospitals should partner with cybersecurity experts to help them assess their security posture, implement security measures, and respond to ransomware attacks.
- Educate employees: Hospitals should educate their employees about the risks of ransomware and how to avoid becoming victims of phishing attacks. Employees should be trained to recognize suspicious emails and to avoid clicking on links or opening attachments from unknown senders.
The Role of Government and Industry
The government and industry also have a role to play in preventing ransomware attacks on hospitals. The government can provide funding for cybersecurity research and development, as well as develop and enforce cybersecurity standards for healthcare providers. Industry can develop and share best practices for cybersecurity, as well as provide hospitals with access to cybersecurity tools and services.
Conclusion
Ransomware attacks are a growing threat to U.S. hospitals, and the consequences can be devastating. Hospitals must take steps to protect themselves from these attacks by implementing strong cybersecurity programs, keeping systems up to date, and educating employees about the risks of ransomware. The government and industry also have a role to play in preventing ransomware attacks on hospitals. By working together, we can help to protect our healthcare system from this growing threat.
The battle against ransomware is an ongoing one, requiring constant vigilance, adaptation, and collaboration. As attackers become more sophisticated, healthcare providers must continually enhance their defenses to protect patient data and ensure the continuity of care. The future of healthcare security depends on a proactive and comprehensive approach to cybersecurity.