“Solar Power Incentives: Driving the Global Energy Transition
Related Articles Solar Power Incentives: Driving the Global Energy Transition
- Ultimate Guide to Attack Surface Reduction: Enhancing Cybersecurity Posture
- Ultimate Endpoint Protection: Shielding Your Network from Cyber Threats
- Solana Gains Traction: A Deep Dive Into The High-Performance Blockchain
- Proven Endpoint Resilience Strategies for Unwavering Cybersecurity
- AI Regulation In The US: Navigating Innovation And Risk
Introduction
On this special occasion, we are happy to review interesting topics related to Solar Power Incentives: Driving the Global Energy Transition. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Solar Power Incentives: Driving the Global Energy Transition
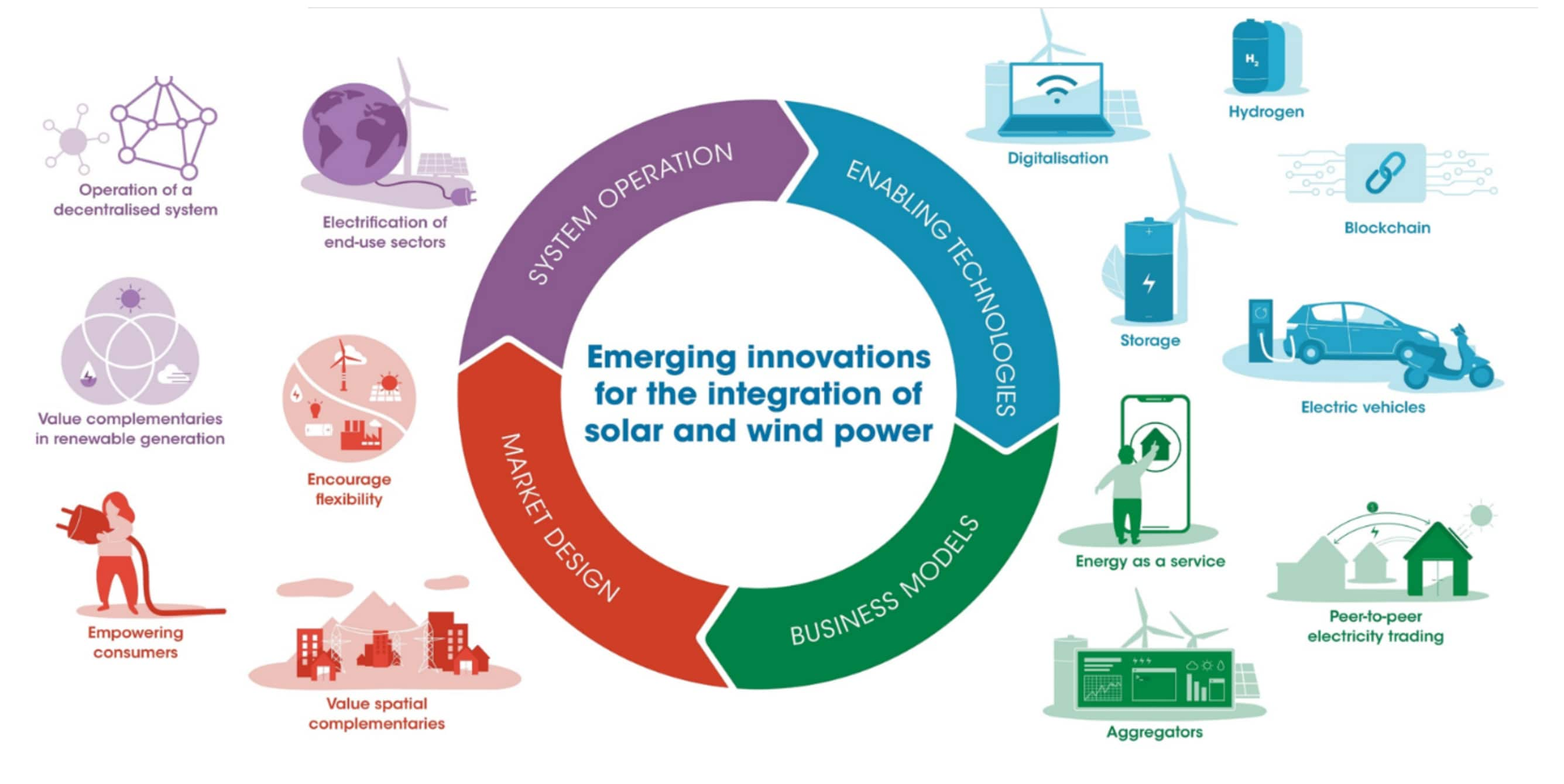
As the world grapples with the urgent need to transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, solar power has emerged as a leading contender. Harnessing the sun’s abundant energy, solar power offers a viable and environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels. However, the adoption of solar power has been significantly influenced by government policies and incentives aimed at accelerating its deployment. These incentives play a crucial role in making solar power more accessible and affordable, driving the global energy transition.
The Rationale Behind Solar Power Incentives
Solar power incentives are government-led initiatives designed to encourage the adoption of solar energy technologies. These incentives address several key barriers that hinder the widespread adoption of solar power, including:
-
High Upfront Costs: Solar power systems often require a significant initial investment, which can be a deterrent for homeowners, businesses, and utilities. Incentives help offset these upfront costs, making solar power more financially attractive.
-
Lack of Awareness and Information: Many potential solar adopters lack sufficient information about the benefits, costs, and technical aspects of solar power. Incentives can include educational programs and outreach efforts to raise awareness and provide guidance.
-
Regulatory and Permitting Hurdles: Complex and time-consuming permitting processes can discourage solar installations. Incentives can streamline these processes, making it easier for individuals and businesses to go solar.
-
Grid Interconnection Challenges: Connecting solar power systems to the grid can be complex and costly. Incentives can help reduce interconnection costs and ensure fair access to the grid.
-
Market Distortions: Fossil fuels often benefit from subsidies and other forms of support, creating an uneven playing field for renewable energy sources like solar power. Incentives help level the playing field and promote fair competition.
Types of Solar Power Incentives
Solar power incentives come in various forms, each designed to address specific barriers and promote different aspects of solar energy adoption. Some of the most common types of incentives include:
-
Tax Credits: Tax credits allow individuals and businesses to deduct a percentage of the cost of a solar power system from their federal or state taxes. Tax credits are a popular and effective incentive, as they directly reduce the cost of going solar.
-
Rebates: Rebates provide a direct cash payment to individuals or businesses after they install a solar power system. Rebates can be offered by federal, state, or local governments, as well as utilities.
-
Grants: Grants are similar to rebates, but they are typically awarded upfront to help cover the initial costs of a solar power system. Grants are often targeted at specific groups, such as low-income households or non-profit organizations.
-
Net Metering: Net metering allows solar power system owners to receive credit for the excess electricity they send back to the grid. This credit can be used to offset their electricity bills, making solar power more cost-effective.
-
Feed-in Tariffs (FITs): Feed-in tariffs guarantee a fixed price for electricity generated by solar power systems. FITs provide long-term revenue certainty, encouraging investment in solar power projects.
-
Property Tax Exemptions: Property tax exemptions reduce or eliminate property taxes on the value of solar power systems. This incentive makes solar power more affordable over the long term.
-
Sales Tax Exemptions: Sales tax exemptions eliminate sales taxes on the purchase of solar power systems. This incentive reduces the upfront cost of going solar.
-
Loan Programs: Loan programs provide low-interest loans to individuals and businesses for the purchase of solar power systems. Loan programs make solar power more accessible to those who cannot afford the upfront costs.
-
Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs): Renewable energy certificates (RECs) represent the environmental benefits of generating electricity from renewable sources like solar power. Solar power system owners can sell RECs to utilities or other entities that need to meet renewable energy mandates.
-
Auctions and Tenders: Governments or utilities can hold auctions or tenders to solicit bids for solar power projects. This competitive process can drive down the cost of solar power and ensure that projects are developed efficiently.
The Impact of Solar Power Incentives
Solar power incentives have had a significant impact on the growth of the solar industry worldwide. They have helped to:
-
Reduce the Cost of Solar Power: Incentives have made solar power more affordable, leading to increased demand and economies of scale. This, in turn, has driven down the cost of solar power systems, making them even more competitive with fossil fuels.
-
Increase Solar Power Adoption: Incentives have encouraged more individuals, businesses, and utilities to adopt solar power. This has led to a significant increase in the amount of solar power capacity installed worldwide.
-
Create Jobs: The solar industry has created hundreds of thousands of jobs in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and other related fields. Incentives have helped to support the growth of the solar industry and create these jobs.
-
Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Solar power generates electricity without emitting greenhouse gases. By encouraging the adoption of solar power, incentives have helped to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change.
-
Promote Energy Independence: Solar power is a domestic energy source that can reduce reliance on imported fossil fuels. Incentives have helped to promote energy independence and security.
Examples of Successful Solar Power Incentive Programs
Many countries and regions have implemented successful solar power incentive programs. Some notable examples include:
-
The Investment Tax Credit (ITC) in the United States: The Investment Tax Credit (ITC) is a federal tax credit that allows individuals and businesses to deduct a percentage of the cost of a solar power system from their federal taxes. The ITC has been instrumental in driving the growth of the solar industry in the United States.
-
The Feed-in Tariff (FIT) in Germany: Germany’s feed-in tariff (FIT) guaranteed a fixed price for electricity generated by solar power systems. The FIT led to a rapid increase in solar power capacity in Germany and helped to make the country a leader in renewable energy.
-
The Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS) in California: California’s Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS) requires utilities to obtain a certain percentage of their electricity from renewable sources. The RPS has helped to drive the demand for solar power in California and has made the state a leader in solar energy.
-
The Net Metering Policy in many countries: Net metering policies that allow solar power system owners to receive credit for the excess electricity they send back to the grid. This policy has helped to make solar power more cost-effective in many countries.
Challenges and Considerations
While solar power incentives have been largely successful, there are also some challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
-
Cost: Solar power incentives can be expensive, and governments need to carefully consider the costs and benefits of these programs.
-
Equity: Incentives should be designed to ensure that they benefit all segments of society, including low-income households and communities.
-
Sustainability: Incentives should be designed to be sustainable over the long term. They should not create market distortions or lead to unsustainable levels of debt.
-
Grid Integration: As the amount of solar power on the grid increases, it is important to ensure that the grid can handle the intermittent nature of solar power. This may require investments in grid infrastructure and energy storage.
-
Policy Stability: Policy stability is crucial for the success of solar power incentives. Sudden changes in incentives can create uncertainty and discourage investment in solar power.
Conclusion
Solar power incentives have played a crucial role in driving the global energy transition. They have helped to reduce the cost of solar power, increase solar power adoption, create jobs, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and promote energy independence. As the world continues to transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, solar power incentives will remain an important tool for accelerating the deployment of solar energy technologies. By carefully designing and implementing these incentives, governments can help to create a cleaner, more sustainable, and more prosperous future for all.
