“Trump’s Tariff Threats Spark Global Trade Disruptions
Related Articles Trump’s Tariff Threats Spark Global Trade Disruptions
- Claudia Sheinbaum Elected As Mexico’s First Female President: A Historic Milestone And A New Chapter For The Nation
- Venezuelan Migrants Return Home Amid Mexico Repatriation Efforts
- Romania Elects Nicușor Dan As President After Annulled Election
- Trump Signs Executive Order To Boost Critical Mineral Production
- Friedrich Merz Elected Chancellor In Historic German Vote
Introduction
On this special occasion, we are happy to review interesting topics related to Trump’s Tariff Threats Spark Global Trade Disruptions. Let’s knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Trump’s Tariff Threats Spark Global Trade Disruptions
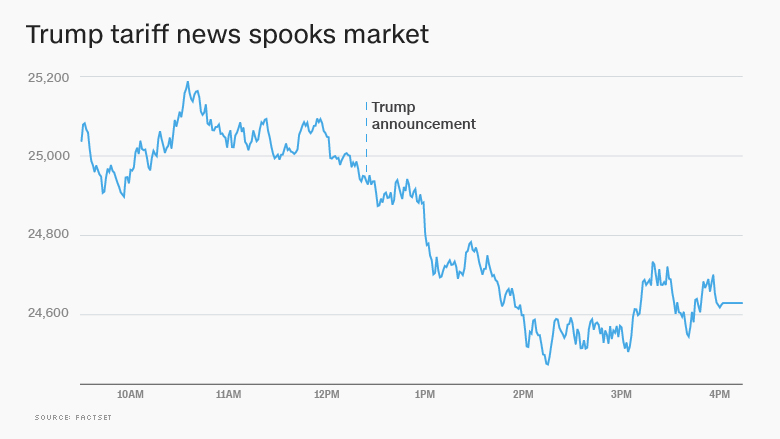
The global economic landscape has been significantly altered in recent years, largely due to the trade policies initiated by former U.S. President Donald Trump. Central to these policies were the imposition and threats of tariffs on goods imported from various countries, including major economic powers such as China, the European Union, and Canada. These actions, intended to protect American industries and reduce trade deficits, have instead triggered a series of disruptions across global trade networks, impacting businesses, consumers, and international relations.
The Rationale Behind Trump’s Tariffs
President Trump’s administration argued that the tariffs were necessary to address what they perceived as unfair trade practices by other nations. Key justifications included:
-
National Security: Certain tariffs, particularly on steel and aluminum, were justified under Section 232 of the Trade Expansion Act of 1962, which allows the president to impose trade restrictions on imports that threaten national security. The argument was that domestic production of these materials was vital for defense and infrastructure.
-
Intellectual Property Protection: The U.S. accused China of widespread intellectual property theft and forced technology transfer. Tariffs were used as a tool to pressure China to strengthen its intellectual property protections and cease these practices.
-
Trade Deficits: A primary goal was to reduce the U.S. trade deficit, which Trump viewed as a sign of economic weakness. By making imports more expensive through tariffs, the administration aimed to encourage domestic production and reduce reliance on foreign goods.
-
Reciprocity: The Trump administration argued that many countries imposed higher tariffs on U.S. goods than the U.S. imposed on their goods. The tariffs were intended to pressure these countries to lower their tariffs and create a more level playing field.
Key Tariff Measures Implemented
The Trump administration implemented several significant tariff measures that had far-reaching effects:
-
Steel and Aluminum Tariffs: In March 2018, the U.S. imposed tariffs of 25% on steel imports and 10% on aluminum imports from most countries. While some countries, like Canada and Mexico, were initially exempted, these exemptions were later revoked and then reinstated after negotiations.
-
China Tariffs: The U.S. imposed tariffs on billions of dollars’ worth of Chinese goods in multiple phases. These tariffs targeted a wide range of products, from industrial components to consumer goods. China retaliated with its own tariffs on U.S. goods, leading to a tit-for-tat trade war.
-
European Union Tariffs: The U.S. imposed tariffs on a variety of EU goods, including agricultural products, in response to disputes over aircraft subsidies (Boeing vs. Airbus) and other trade issues. The EU also retaliated with tariffs on U.S. goods.
Impact on Global Trade and Economy
The imposition of tariffs by the U.S. and retaliatory measures by other countries have had several significant impacts on global trade and the economy:
-
Increased Costs for Businesses and Consumers: Tariffs increase the cost of imported goods, which can lead to higher prices for businesses that rely on these goods as inputs. These increased costs are often passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices for finished products.
-
Disruptions to Supply Chains: Tariffs can disrupt global supply chains by making it more expensive or difficult to source goods from certain countries. This can lead to delays, shortages, and increased uncertainty for businesses.
-
Reduced Trade Flows: The imposition of tariffs has led to a decrease in trade between the U.S. and countries targeted by the tariffs. This can negatively impact economic growth in both the U.S. and these countries.
-
Increased Uncertainty: The unpredictable nature of tariff policies has created a climate of uncertainty for businesses, making it difficult for them to plan for the future. This uncertainty can discourage investment and slow economic growth.
-
Retaliatory Measures: The imposition of tariffs by the U.S. has led to retaliatory measures by other countries, resulting in a trade war that has further disrupted global trade and economic activity.
-
Impact on Specific Industries: Certain industries have been particularly hard hit by the tariffs. For example, the agricultural sector has suffered due to retaliatory tariffs imposed by China on U.S. agricultural products.
-
WTO Disputes: Many of the tariffs imposed by the U.S. have been challenged by other countries at the World Trade Organization (WTO). These disputes can take years to resolve and can further strain international trade relations.
Case Studies: Specific Examples of Disruption
-
The Steel and Aluminum Industries: The tariffs on steel and aluminum were intended to protect domestic producers. While some U.S. steel and aluminum companies did see an initial boost, downstream industries that rely on these materials, such as the automotive and construction sectors, faced higher costs. These higher costs reduced their competitiveness and, in some cases, led to job losses.
-
The Agricultural Sector: U.S. farmers were significantly impacted by retaliatory tariffs imposed by China on agricultural products such as soybeans, corn, and pork. These tariffs reduced U.S. agricultural exports to China, leading to lower prices for farmers and financial hardship in rural communities. The U.S. government provided billions of dollars in aid to farmers to offset these losses.
-
The Automotive Industry: The automotive industry, which relies on complex global supply chains, was heavily affected by the tariffs. Tariffs on steel and aluminum increased production costs, while tariffs on auto parts imported from other countries made it more expensive to manufacture cars in the U.S. This led to higher prices for consumers and reduced competitiveness for U.S. automakers.
The Broader Geopolitical Implications
The trade policies of the Trump administration have had broader geopolitical implications:
-
Strained International Relations: The imposition of tariffs and the resulting trade disputes have strained relations between the U.S. and many of its key trading partners, including China, the EU, and Canada.
-
Weakened Multilateral Institutions: The Trump administration’s frequent use of unilateral trade measures and its criticism of the WTO have weakened multilateral institutions and undermined the rules-based international trading system.
-
Shift in Global Power Dynamics: The trade disputes have accelerated a shift in global power dynamics, with China seeking to position itself as a champion of free trade and multilateralism.
-
Reassessment of Supply Chains: The disruptions caused by the tariffs have led many companies to reassess their supply chains and consider diversifying their sourcing to reduce their reliance on any single country or region.
The Biden Administration’s Approach
The Biden administration has taken a somewhat different approach to trade policy than its predecessor. While it has maintained some of the tariffs imposed by the Trump administration, it has also sought to engage in dialogue and negotiations with other countries to address trade issues. Key aspects of the Biden administration’s trade policy include:
-
Focus on Allies: The Biden administration has prioritized strengthening trade relations with allies, such as the EU and Japan.
-
Emphasis on Labor and Environmental Standards: The administration has emphasized the importance of including labor and environmental standards in trade agreements.
-
Strategic Competition with China: While seeking to avoid a full-blown trade war, the Biden administration has maintained a firm stance on China’s trade practices and has focused on strategic competition in areas such as technology and innovation.
-
Review of Trade Policies: The administration has initiated a review of U.S. trade policies to ensure that they are aligned with its economic and strategic goals.
Long-Term Consequences and Future Outlook
The long-term consequences of Trump’s tariff policies are still unfolding, but some trends are becoming clear:
-
Permanent Changes to Supply Chains: The disruptions caused by the tariffs have led many companies to make permanent changes to their supply chains, reducing their reliance on China and other countries targeted by the tariffs.
-
Increased Regionalization of Trade: The trade disputes have encouraged the regionalization of trade, with countries seeking to strengthen trade ties with their neighbors.
-
Greater Focus on Domestic Production: The tariffs have incentivized some companies to increase domestic production, leading to a resurgence of manufacturing in the U.S.
-
Ongoing Trade Tensions: Trade tensions between the U.S. and China are likely to persist for the foreseeable future, even if the two countries are able to reach some form of trade agreement.
The future of global trade will depend on how the U.S. and other major economic powers navigate these challenges. A return to a rules-based international trading system is essential for promoting economic growth and stability. However, this will require a willingness to address legitimate concerns about unfair trade practices and to reform the WTO to make it more effective in the 21st century.
In conclusion, Trump’s tariff threats and subsequent implementation have had a profound and multifaceted impact on global trade. While intended to address perceived unfair trade practices and protect domestic industries, these measures have instead triggered disruptions to supply chains, increased costs for businesses and consumers, and strained international relations. The long-term consequences of these policies are still unfolding, but they have undoubtedly reshaped the global economic landscape and highlighted the need for a more cooperative and rules-based approach to international trade.

Pingback: 2025 UK Wildfires Surge Amid Record Heat: A Nation Ablaze – DAYLI NEWS