“US Government Policies: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles US Government Policies: A Comprehensive Overview
- The Crypto Market Structure Bill: A Comprehensive Overview
- Mpox Cases Increasing: A Global Health Concern Revisited
- Cathy Doll X Faye: A Deep Dive Into The Collaboration, Products, And Impact
- 2025 Grammy Awards: A Night Of Triumphs Marred By Controversy
- Microsoft’s Acquisition Spree: A Deep Dive Into Strategic Growth And Market Dominance
Introduction
We will be happy to explore interesting topics related to US Government Policies: A Comprehensive Overview. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
US Government Policies: A Comprehensive Overview
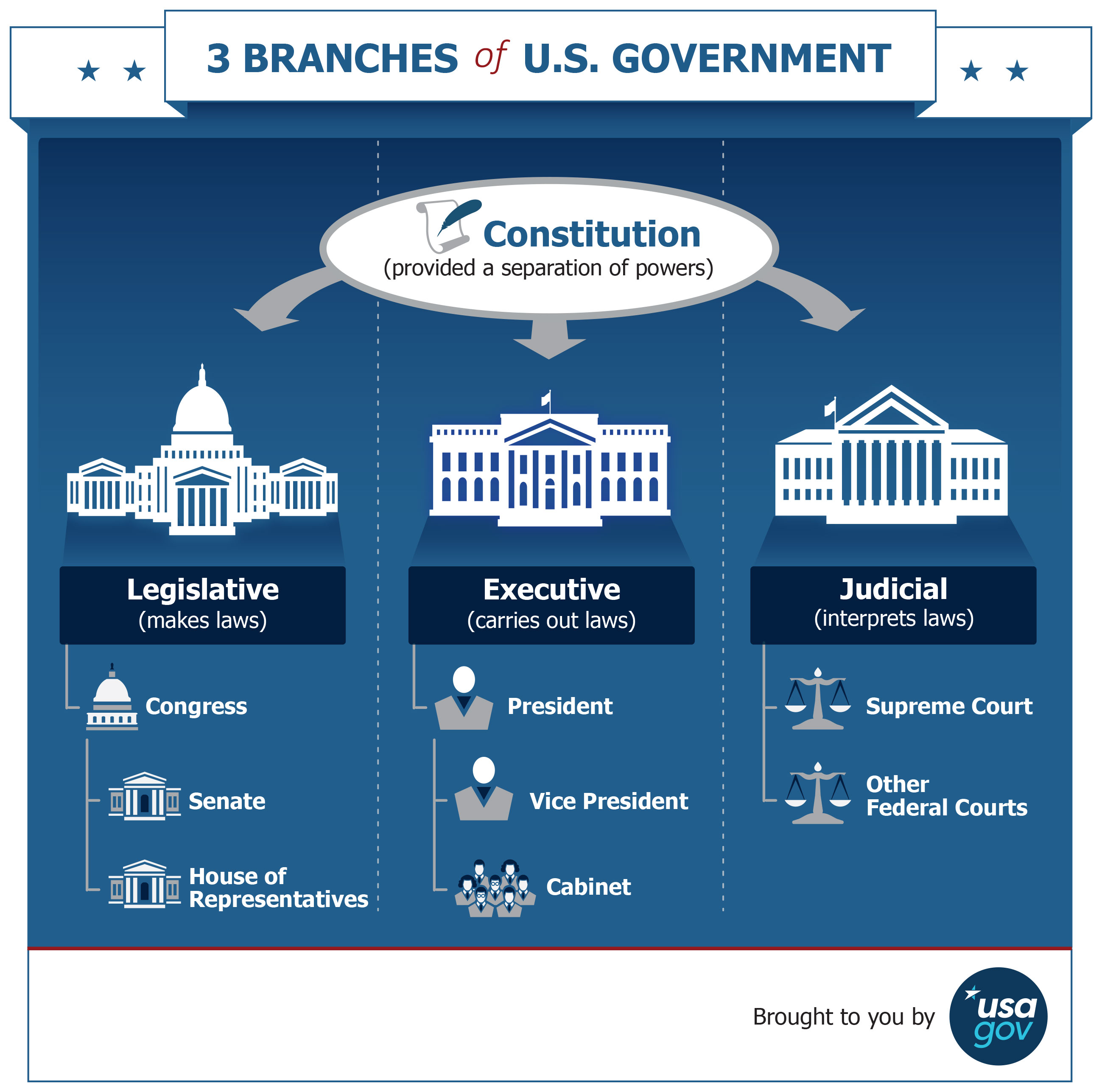
US government policies form the backbone of the nation’s governance, influencing various aspects of American life, from the economy and healthcare to education and foreign relations. These policies are the product of complex interactions between the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, shaped by political ideologies, public opinion, and historical context. Understanding US government policies requires examining their formation, implementation, and impact on society.
Policy Formation
The process of policy formation in the US government is multifaceted and involves several key players:
-
Legislative Branch: Congress, composed of the Senate and the House of Representatives, is responsible for drafting and enacting laws. Legislators introduce bills, hold hearings, debate, and vote on proposed legislation. The committee system plays a crucial role in shaping policy, as committees conduct research, gather expert testimony, and make recommendations to the full chamber.
-
Executive Branch: The President, as the head of the executive branch, plays a significant role in shaping policy through various means. The President can propose legislation to Congress, issue executive orders, and influence policy through the power of persuasion. Federal agencies, such as the Department of Health and Human Services and the Environmental Protection Agency, are responsible for implementing and enforcing policies within their respective areas of expertise.
-
Judicial Branch: The judicial branch, led by the Supreme Court, interprets laws and ensures their constitutionality. Judicial review, the power of the courts to declare laws unconstitutional, can significantly impact policy by striking down laws or shaping their interpretation.
-
Interest Groups and Lobbyists: Interest groups and lobbyists advocate for specific policies by providing information to policymakers, mobilizing public support, and contributing to political campaigns. These groups represent a wide range of interests, including businesses, labor unions, environmental organizations, and advocacy groups.
-
Public Opinion: Public opinion can influence policy formation through various channels, including elections, public protests, and social media. Policymakers often consider public sentiment when making decisions, as public support can be crucial for the success of policy initiatives.
Types of US Government Policies
US government policies can be broadly categorized into several types:
-
Economic Policies: Economic policies aim to promote economic growth, stability, and full employment. These policies include fiscal policy, which involves government spending and taxation, and monetary policy, which involves managing the money supply and interest rates. Examples of economic policies include tax cuts, infrastructure spending, and regulations on financial institutions.
-
Social Policies: Social policies address issues related to social welfare, healthcare, education, and civil rights. These policies aim to promote social equity, protect vulnerable populations, and improve the overall quality of life. Examples of social policies include Social Security, Medicare, Medicaid, and the Affordable Care Act.
-
Environmental Policies: Environmental policies aim to protect the environment, conserve natural resources, and mitigate the effects of pollution and climate change. These policies include regulations on air and water quality, protection of endangered species, and promotion of renewable energy sources. Examples of environmental policies include the Clean Air Act, the Clean Water Act, and the Endangered Species Act.
-
Foreign Policies: Foreign policies guide the US government’s interactions with other countries. These policies include diplomacy, trade agreements, military alliances, and foreign aid. Foreign policies aim to promote US interests, maintain international security, and foster global cooperation. Examples of foreign policies include the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), trade agreements with other countries, and foreign aid programs.
Impact of US Government Policies
US government policies have a profound impact on various aspects of American society:
-
Economy: Economic policies can influence economic growth, employment rates, inflation, and income inequality. For example, tax cuts can stimulate economic growth but may also increase income inequality. Government spending on infrastructure can create jobs and boost economic activity.
-
Healthcare: Healthcare policies can affect access to healthcare, healthcare costs, and the quality of healthcare services. The Affordable Care Act, for example, expanded health insurance coverage to millions of Americans but has also been criticized for increasing healthcare costs.
-
Education: Education policies can influence the quality of education, access to education, and educational outcomes. Policies such as No Child Left Behind and the Every Student Succeeds Act have aimed to improve educational standards and accountability.
-
Environment: Environmental policies can protect the environment, conserve natural resources, and mitigate the effects of pollution and climate change. The Clean Air Act, for example, has significantly reduced air pollution in the United States.
-
Social Welfare: Social welfare policies can provide a safety net for vulnerable populations, reduce poverty, and promote social equity. Social Security, for example, provides retirement, disability, and survivor benefits to millions of Americans.
-
Foreign Relations: Foreign policies can shape the US government’s relationships with other countries, influence international events, and promote US interests abroad. The US government’s foreign policies have played a significant role in shaping the global political landscape.
Challenges and Controversies
US government policies are often subject to challenges and controversies:
-
Political Polarization: Political polarization can make it difficult to reach consensus on policy issues. The increasing divide between Democrats and Republicans has led to gridlock and difficulty in enacting legislation.
-
Budget Constraints: Budget constraints can limit the government’s ability to address pressing policy issues. The national debt and budget deficits can make it difficult to fund new programs or expand existing ones.
-
Special Interests: Special interests can exert undue influence on policy formation, leading to policies that benefit narrow interests at the expense of the public good. Lobbying and campaign contributions can give special interests an advantage in shaping policy.
-
Implementation Challenges: Implementing policies can be challenging, as policies may encounter resistance from individuals, businesses, or other government agencies. Effective implementation requires careful planning, coordination, and oversight.
-
Unintended Consequences: Policies can have unintended consequences that are difficult to predict or control. Policymakers must carefully consider the potential unintended consequences of their actions and be prepared to adjust policies as needed.
Examples of Key US Government Policies
-
Social Security Act of 1935: Established a system of old-age benefits for workers, benefits for victims of industrial accidents, unemployment insurance, aid for dependent mothers and children, and grants to states to provide various forms of social welfare.
-
Civil Rights Act of 1964: Prohibits discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin. It ended segregation in public places and prohibited employment discrimination.
-
Medicare and Medicaid (1965): Medicare provides health insurance for the elderly and disabled, while Medicaid provides healthcare for low-income individuals and families.
-
Clean Air Act (1970): Regulates air emissions from stationary and mobile sources. It has significantly reduced air pollution in the United States.
-
Affordable Care Act (2010): Expanded health insurance coverage to millions of uninsured Americans. It also implemented reforms to the healthcare system aimed at improving quality and reducing costs.
-
Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (2010): Reformed the financial system to prevent another financial crisis. It created new regulatory agencies and implemented new rules for financial institutions.
Conclusion
US government policies play a vital role in shaping American society. Understanding the formation, implementation, and impact of these policies is essential for informed citizenship and effective participation in the democratic process. By engaging in thoughtful debate and holding policymakers accountable, citizens can help ensure that government policies serve the best interests of the nation. The ongoing evolution of these policies reflects the dynamic nature of American society and the constant need to address new challenges and opportunities. As such, continuous evaluation and adaptation of policies are necessary to meet the changing needs of the nation and its citizens.