“US Labor Market: Navigating a Landscape of Resilience, Shifts, and Uncertainty
Related Articles US Labor Market: Navigating a Landscape of Resilience, Shifts, and Uncertainty
- Crypto Market Structure Bill: A Transformative Step Or Regulatory Overreach?
- Apple Unleashes Innovation: A Deep Dive Into The Latest Product Lineup
- East Coast Swelters Under Oppressive Heat Wave
- AI In National Defense: Revolutionizing Warfare And Raising Ethical Dilemmas
- Mastering Incident Response: A Guide to Mitigating Cyber Threats
Introduction
On this special occasion, we are happy to review interesting topics related to US Labor Market: Navigating a Landscape of Resilience, Shifts, and Uncertainty. Let’s knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
US Labor Market: Navigating a Landscape of Resilience, Shifts, and Uncertainty

The US labor market has been a subject of intense scrutiny in recent years, marked by unprecedented disruptions, rapid recoveries, and persistent questions about its future trajectory. From the depths of the COVID-19 pandemic to the challenges of inflation and evolving work patterns, the labor market has demonstrated remarkable resilience while also undergoing significant transformations. This article provides an in-depth look at the current state of the US labor market, examining key indicators, emerging trends, and the factors shaping its evolution.
Key Indicators: A Snapshot of the Present
To understand the health and dynamics of the US labor market, it’s essential to monitor several key indicators:
-
Unemployment Rate: This is perhaps the most widely followed metric, representing the percentage of the labor force that is actively seeking employment but unable to find it. As of October 2023, the unemployment rate stood at 3.9%, indicating a relatively tight labor market. This is a significant improvement from the peak of 14.7% in April 2020 but slightly above the pre-pandemic level of around 3.5%.
-
Job Openings: The number of job openings provides insight into the demand for labor. A high number of job openings suggests that employers are actively seeking to hire, indicating a strong labor market. In recent months, job openings have remained elevated but have shown signs of cooling off from their historic highs.
-
Labor Force Participation Rate: This measures the percentage of the civilian noninstitutional population that is either employed or actively seeking employment. A higher participation rate indicates a greater proportion of the population is engaged in the labor market. The labor force participation rate has been gradually recovering since the pandemic but remains slightly below pre-pandemic levels.
-
Wage Growth: Wage growth reflects the rate at which earnings are increasing. Strong wage growth can be a sign of a healthy labor market, but it can also contribute to inflationary pressures. Wage growth has been elevated in recent years, driven by tight labor market conditions and increased demand for workers.
-
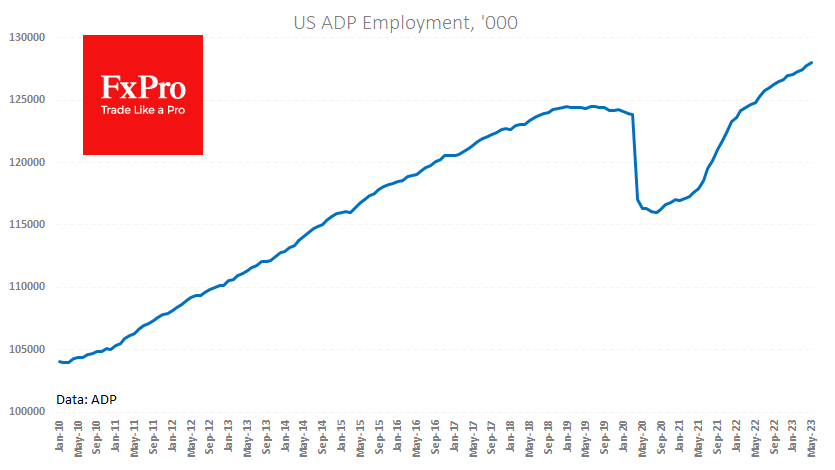
Nonfarm Payroll Employment: This measures the number of workers in the US excluding farm workers, private household employees, and non-profit employees. It is a key indicator of job creation and economic growth.
Recent Trends: Shaping the Labor Market Landscape
Several key trends are shaping the US labor market:
-
The Great Resignation/Shuffle: The COVID-19 pandemic triggered a wave of resignations as workers reevaluated their priorities and sought better opportunities, higher pay, or more flexible work arrangements. This phenomenon, often referred to as the "Great Resignation" or "Great Shuffle," has led to increased turnover and competition for talent.
-
Remote Work and Hybrid Models: The pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote work, and many companies have embraced hybrid models that combine remote and in-office work. This shift has had a profound impact on the labor market, influencing where people choose to live and work, and creating new opportunities for workers in different geographic locations.
-
Skills Gap and Talent Shortages: Many employers are struggling to find workers with the skills they need, particularly in areas such as technology, healthcare, and manufacturing. This skills gap is driven by factors such as technological advancements, changing job requirements, and a lack of qualified candidates.
-
Automation and Artificial Intelligence: Automation and AI are transforming the nature of work, automating routine tasks and creating new opportunities for workers with specialized skills. While some fear that automation will lead to job losses, others believe it will create new jobs and increase productivity.
-
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI): DEI has become an increasingly important consideration for employers as they seek to attract and retain talent. Companies are implementing DEI initiatives to create more inclusive workplaces and address systemic inequalities.
-
The Gig Economy: The gig economy, characterized by short-term contracts or freelance work, continues to grow. While it offers flexibility for some workers, it also raises concerns about job security and benefits.
-
Aging Workforce: The aging of the US population is creating challenges for the labor market. As baby boomers retire, there are fewer workers to replace them, leading to labor shortages in some sectors.
Factors Influencing the Labor Market
Several factors are influencing the US labor market:
-
Economic Growth: Economic growth is a primary driver of job creation. A strong economy typically leads to increased demand for labor and lower unemployment rates.
-
Government Policies: Government policies, such as tax policies, regulations, and investments in education and infrastructure, can have a significant impact on the labor market.
-
Technological Advancements: Technological advancements are transforming the nature of work, creating new jobs and displacing others.
-
Demographic Trends: Demographic trends, such as the aging of the population and changes in immigration patterns, can affect the size and composition of the labor force.
-
Global Economic Conditions: Global economic conditions, such as trade policies and international competition, can influence the demand for US goods and services and, therefore, the demand for labor.
-
Inflation and Interest Rates: The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy, particularly its decisions on interest rates, can influence economic growth and the labor market. High inflation can lead to tighter monetary policy, which can slow economic growth and increase unemployment.
Challenges and Opportunities
The US labor market faces several challenges and opportunities:
-
Addressing the Skills Gap: Addressing the skills gap is critical to ensuring that workers have the skills they need to succeed in the changing economy. This requires investments in education and training programs, as well as collaboration between employers and educational institutions.
-
Promoting Equitable Access to Opportunities: Ensuring that all workers have equal access to opportunities is essential for creating a fair and inclusive labor market. This requires addressing systemic inequalities and promoting DEI initiatives.
-
Adapting to Technological Change: Adapting to technological change is crucial for ensuring that workers are prepared for the jobs of the future. This requires investments in lifelong learning and skills development.
-
Supporting Workers in the Gig Economy: Finding ways to support workers in the gig economy is important for ensuring that they have access to job security, benefits, and fair wages.
-
Managing the Aging Workforce: Managing the aging workforce requires strategies to retain older workers, attract younger workers, and address the challenges of labor shortages.
Expert Perspectives
Economists and labor market experts offer a range of perspectives on the current state of the US labor market:
-
Some economists believe that the labor market is fundamentally strong, with low unemployment and rising wages. They argue that the current challenges are temporary and that the labor market will continue to improve as the economy recovers.
-
Other economists are more cautious, pointing to factors such as inflation, rising interest rates, and global economic uncertainty as potential headwinds for the labor market. They argue that the labor market could weaken in the coming months.
-
Labor market experts emphasize the importance of addressing the skills gap, promoting equitable access to opportunities, and adapting to technological change. They argue that these are critical for ensuring that the US labor market remains competitive and inclusive.
Conclusion
The US labor market is a dynamic and complex landscape shaped by a variety of factors. While it has demonstrated remarkable resilience in recent years, it also faces significant challenges and opportunities. By monitoring key indicators, understanding emerging trends, and addressing the challenges, policymakers, employers, and workers can work together to create a labor market that is strong, inclusive, and adaptable to the changing needs of the economy. The future of the US labor market will depend on how well these challenges are met and how effectively the opportunities are seized.