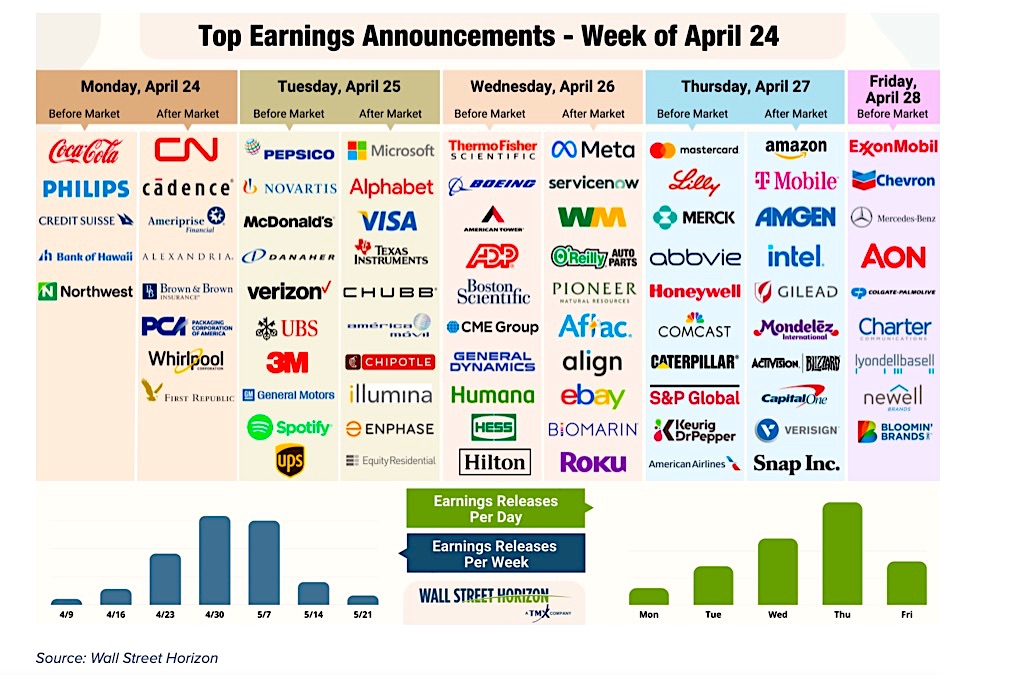
“Wall Street Earnings Reports: A Deep Dive into Financial Performance and Market Impact
Related Articles Wall Street Earnings Reports: A Deep Dive into Financial Performance and Market Impact
- Cyber Breach Response: A Comprehensive Guide to Protecting Your Organization
- Comprehensive Cybersecurity Solutions for Enhanced Online Security
- Master the Art of Advanced Threat Protection: Your Cybersecurity Fortress
- Biden’s Approval Rating In May 2025: A Mid-Term Assessment And Future Projections
- Network Security: The Ultimate Guide to Protecting Your Business
Introduction
With great enthusiasm, let’s explore interesting topics related to Wall Street Earnings Reports: A Deep Dive into Financial Performance and Market Impact. Come on knit interesting information and provide new insights to readers.
Table of Content
Wall Street Earnings Reports: A Deep Dive into Financial Performance and Market Impact
Wall Street earnings reports are a crucial aspect of the financial world, providing a detailed look into the financial performance of publicly traded companies. These reports, released quarterly, offer valuable insights into a company’s revenue, expenses, profitability, and future prospects. Investors, analysts, and the media closely scrutinize these reports to make informed decisions about buying, selling, or holding stocks.
Understanding Earnings Reports
An earnings report, also known as a 10-Q report (quarterly) or 10-K report (annual), is a comprehensive document that reveals a company’s financial performance over a specific period. It includes several key components:
-
Income Statement: This statement, also known as the profit and loss (P&L) statement, summarizes a company’s revenues, expenses, and net income (or loss) over a period. It provides a clear picture of a company’s profitability.
-
Balance Sheet: The balance sheet is a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity at a specific point in time. It follows the basic accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity.
-
Cash Flow Statement: This statement tracks the movement of cash both into and out of a company. It’s divided into three sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities.
-
Management Discussion and Analysis (MD&A): In this section, management discusses the company’s performance, strategies, and outlook. It provides context and insights into the financial results.
-
Notes to Financial Statements: These notes provide additional details and explanations about the numbers presented in the financial statements. They often include information about accounting policies, debt, and other significant items.
Key Metrics to Watch
When analyzing earnings reports, several key metrics are particularly important:
-
Revenue: Revenue, also known as sales, is the total amount of money a company earns from its primary business activities. It’s a top-line number that indicates the company’s ability to generate sales.
-
Earnings per Share (EPS): EPS is a company’s net income divided by the number of outstanding shares. It’s a key measure of profitability on a per-share basis.
-
Net Income: Net income is the company’s profit after all expenses, including taxes, have been deducted from revenue. It represents the bottom line of the income statement.
-
Gross Margin: Gross margin is the difference between revenue and the cost of goods sold (COGS), expressed as a percentage of revenue. It indicates the company’s efficiency in producing goods or services.
-
Operating Margin: Operating margin is the ratio of operating income to revenue. It measures a company’s profitability from its core operations, excluding interest and taxes.
-
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: The P/E ratio is the ratio of a company’s stock price to its earnings per share. It’s a valuation metric that indicates how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of earnings.
-
Debt-to-Equity Ratio: This ratio measures a company’s total debt relative to its shareholders’ equity. It provides insights into the company’s financial leverage and risk.
The Earnings Season
Earnings season is the period each quarter when most publicly traded companies release their earnings reports. It typically begins a few weeks after the end of each quarter (March, June, September, and December). During earnings season, trading volumes tend to increase, and market volatility can be higher as investors react to the news.
Impact on Stock Prices
Earnings reports have a significant impact on stock prices. When a company announces earnings that exceed analysts’ expectations, its stock price often rises. Conversely, if earnings fall short of expectations, the stock price may decline. However, the market’s reaction to earnings reports can be complex and influenced by factors such as:
-
Expectations: The market’s expectations play a crucial role. If a company is widely expected to perform well, even a good earnings report may not lead to a significant stock price increase if it merely meets expectations.
-
Guidance: Companies often provide guidance about their expected future performance. Positive guidance can boost investor confidence, while negative guidance can dampen sentiment.
-
Overall Market Conditions: The broader market environment can influence how investors react to earnings reports. During a bull market, investors may be more forgiving of disappointing earnings, while during a bear market, they may be more critical.
-
Sector Trends: The performance of a company’s sector can also affect its stock price. If the sector is doing well, investors may be more optimistic about the company’s prospects.
The Role of Analysts
Analysts play a crucial role in interpreting earnings reports and providing recommendations to investors. They conduct in-depth research on companies, analyze their financial statements, and make forecasts about their future performance. Analysts’ ratings, price targets, and earnings estimates can influence investor sentiment and stock prices.
Strategies for Investors
Investors can use earnings reports to make informed decisions about their investments. Here are a few strategies:
-
Do Your Homework: Before investing in a company, thoroughly research its financial statements, business model, and competitive landscape.
-
Understand Expectations: Pay attention to analysts’ expectations and market sentiment. A company’s stock price may already reflect anticipated earnings.
-
Focus on Long-Term Trends: Don’t get too caught up in short-term fluctuations. Focus on the company’s long-term growth potential and competitive advantages.
-
Consider Valuation: Evaluate the company’s valuation metrics, such as the P/E ratio, to determine whether it is fairly priced.
-
Diversify Your Portfolio: Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Diversify your portfolio across different sectors and asset classes to reduce risk.
Challenges and Limitations
While earnings reports provide valuable information, they also have limitations:
-
Accounting Manipulation: Companies can sometimes manipulate their accounting practices to present a more favorable picture of their financial performance.
-
Backward-Looking: Earnings reports are backward-looking, reflecting past performance. They may not accurately predict future results.
-
Subjectivity: Some aspects of financial reporting, such as estimates and judgments, are subjective and can vary from company to company.
-
Complexity: Analyzing earnings reports can be complex and time-consuming. Investors may need to consult with financial professionals for assistance.
The Future of Earnings Reports
As technology evolves, the way earnings reports are presented and analyzed is also changing. Here are a few trends to watch:
-
Real-Time Data: Investors are increasingly demanding real-time data and insights. Companies may need to provide more frequent and timely updates on their financial performance.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI and machine learning can be used to analyze earnings reports more efficiently and identify patterns and anomalies.
-
Alternative Data: Investors are also using alternative data sources, such as social media sentiment and web traffic, to supplement traditional financial data.
-
ESG Reporting: Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors are becoming increasingly important to investors. Companies may need to provide more detailed disclosures about their ESG performance.
In conclusion, Wall Street earnings reports are a critical source of information for investors, analysts, and the media. By understanding the key components of earnings reports, analyzing important metrics, and considering the broader market context, investors can make informed decisions about their investments. However, it’s essential to be aware of the limitations of earnings reports and to conduct thorough research before investing in any company.